Cytoplasmic N-terminal protein acetylation is required for efficient photosynthesis in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 12897255
- PMCID: PMC167172
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.012377
Cytoplasmic N-terminal protein acetylation is required for efficient photosynthesis in Arabidopsis
Abstract
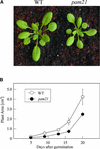
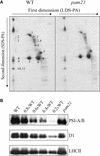
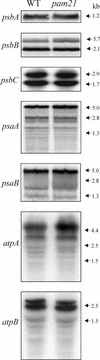
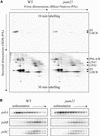
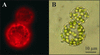
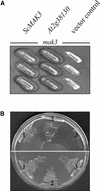
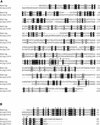
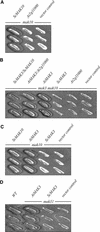
The Arabidopsis atmak3-1 mutant was identified on the basis of a decreased effective quantum yield of photosystem II. In atmak3-1, the synthesis of the plastome-encoded photosystem II core proteins D1 and CP47 is affected, resulting in a decrease in the abundance of thylakoid multiprotein complexes. DNA array-based mRNA analysis indicated that extraplastid functions also are altered. The mutation responsible was localized to AtMAK3, which encodes a homolog of the yeast protein Mak3p. In yeast, Mak3p, together with Mak10p and Mak31p, forms the N-terminal acetyltransferase complex C (NatC). The cytoplasmic AtMAK3 protein can functionally replace Mak3p, Mak10p, and Mak31p in acetylating N termini of endogenous proteins and the L-A virus Gag protein. This result, together with the finding that knockout of the Arabidopsis MAK10 homolog does not result in obvious physiological effects, indicates that AtMAK3 function does not require NatC complex formation, as it does in yeast. We suggest that N-acetylation of certain chloroplast precursor protein(s) is necessary for the efficient accumulation of the mature protein(s) in chloroplasts.
Figures



References
-
- Arnold, R.J., Polevoda, B., Reilly, J.P., and Sherman, F. (1999). The action of N-terminal acetyltransferases on yeast ribosomal proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 37035–37040. - PubMed
-
- Barkan, A. (1998). Approaches to investigating nuclear genes that function in chloroplast biogenesis in land plants. Methods Enzymol. 297, 38–57.
-
- Bassi, R., dal Belin Peruffo, A., Barbato, R., and Ghisi, R. (1985). Differences in chlorophyll-protein complexes and composition of polypeptides between thylakoids from bundle sheaths and mesophyll cells in maize. Eur. J. Biochem. 146, 589–595. - PubMed
-
- Choquet, Y., and Wollman, F.A. (2002). Translational regulations as specific traits of chloroplast gene expression. FEBS Lett. 529, 39–42. - PubMed
-
- Clough, S.J., and Bent, A.F. (1998). Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 16, 735–743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

