Coupling the cell cycle to cell growth
- PMID: 12897798
- PMCID: PMC1326335
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.embor895
Coupling the cell cycle to cell growth
Abstract
In order to multiply, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells go through a series of events that are collectively called the cell cycle. However, DNA replication, mitosis and cell division may also be viewed as having their own, in principle independent, cycles, which are tied together by mechanisms extrinsic to the cell cycle--the checkpoints--that maintain the order of events. We propose that our understanding of cell-cycle regulation is enhanced by viewing each event individually, as an independently regulated process. The nature of the parameters that regulate cell-cycle events is discussed and, in particular, we argue that cell mass is not such a parameter.
Figures
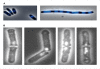
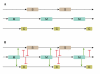
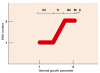


References
-
- Bernander R. ( 1994) Universal cell cycle regulation? Trends Cell Biol., 4, 76–79. - PubMed
-
- Carlson C.R., Grallert B., Stokke T. & Boye E. ( 1999) Regulation of the start of DNA replication in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J. Cell Sci., 112, 939–946. - PubMed
-
- Conlon I.J., Dunn G.A., Mudge A.W. & Raff M.C. ( 2001) Extracellular control of cell size. Nature Cell Biol., 3, 918–921. - PubMed
-
- Cooper S. & Helmstetter C.E. ( 1968) Chromosome replication and the division cycle of Escherichia coli B/r. J. Mol. Biol., 31, 519–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

