Gamma delta T cells provide an early source of interferon gamma in tumor immunity
- PMID: 12900519
- PMCID: PMC2194096
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20030584
Gamma delta T cells provide an early source of interferon gamma in tumor immunity
Abstract
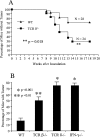
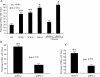
Interferon (IFN)-gamma is necessary for tumor immunity, however, its initial cellular source is unknown. Because gammadelta T cells primarily produce this cytokine upon activation, we hypothesized that they would provide an important early source of IFN-gamma in tumor immunosurveillance. To address this hypothesis, we first demonstrated that gammadelta T cell-deficient mice had a significantly higher incidence of tumor development after challenge with a chemical carcinogen methylcholanthrene (MCA) or inoculation with the melanoma cell line B16. In wild-type mice, gammadelta T cells were recruited to the site of tumor as early as day 3 after inoculation, followed by alphabeta T cells at day 5. We then used bone marrow chimeras and fetal liver reconstitutions to create mice with an intact gammadelta T cell repertoire but one that was specifically deficient in the capacity to produce IFN-gamma. Such mice had a higher incidence of tumor development, induced either with MCA or by inoculation of B16 melanoma cells, compared with mice with IFN-gamma-competent gammadelta T cells. Moreover, genetic deficiency of gammadelta T cells resulted in impaired IFN-gamma production by tumor antigen-triggered alphabeta T cell upon immunization with tumor lysate. These results demonstrate that gammadelta T cells can play a necessary role in tumor immunity through provision of an early source of IFN-gamma that in turn may regulate the function of tumor-triggered alphabeta T cells.
Figures



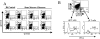

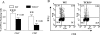
References
-
- Ikeda, H., L.J. Old, and R.D. Schreiber. 2002. The roles of IFN gamma in protection against tumor development and cancer immunoediting. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 13:95–109. - PubMed
-
- Dunn, G.P., A.T. Bruce, H. Ikeda, L.J. Old, and R.D. Schreiber. 2002. Cancer immunoediting: from immunosurveillance to tumor escape. Nat. Immunol. 3:991–998. - PubMed
-
- Street, S.E., E. Cretney, and M.J. Smyth. 2001. Perforin and interferon-gamma activities independently control tumor initiation, growth, and metastasis. Blood. 97:192–197. - PubMed
-
- Shankaran, V., H. Ikeda, A.T. Bruce, J.M. White, P.E. Swanson, L.J. Old, and R.D. Schreiber. 2001. IFNgamma and lymphocytes prevent primary tumour development and shape tumour immunogenicity. Nature. 410:1107–1111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

