Angiotensin II-acetylcholine noncovalent complexes analyzed with MALDI-ion mobility-TOF MS
- PMID: 12901606
- PMCID: PMC2279889
Angiotensin II-acetylcholine noncovalent complexes analyzed with MALDI-ion mobility-TOF MS
Abstract
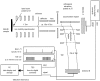
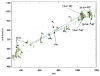
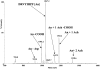
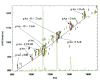
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-ion mobility-orthogonal time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-IM oTOF MS) is a new technique that allows laser desorbed ion to be preseparated on the basis of their shape prior to mas analysis. Using this instrument, we tested the postulate that addition of a quaternary ammonium compound such as acetylcholine to the model phosphorylated peptide angio tensin II would enhance its detection by MALDI in two ways. First of all, the acetylcholine-peptide complex could ionize more efficiently than the bare phosphopeptide. Furthermore the ion mobility could separate the complex ion on the basis of its charge/volume from isobaric interferences, which would otherwise limit detection sensitivity.
Figures

References
-
- Srebalus CA, Li J, Marshall WS, Clemmer DE. Gas-phase separations of electrosprayed peptide libraries. Anal Chem 1999;71:3918–3927. - PubMed
-
- Wu C, Siems WF, Asbury RG, Hill HH. Secondary electrospray ionization ion mobility spectrometry/mass spectrometry of illicit drugs. Anal Chem 1998;70:4929–4938. - PubMed
-
- Valentine SJ, Anderson JG, Ellington AD, Clemmer DE. Disulfide-intact and -reduced lysozyme in the gas phase: conformations and pathways of folding and unfolding. J Phys Chem B 1997;101:3891–3900.
-
- Kinnear BS, Jarrold MF. Helix formation in unsolvated peptides: side chain entropy is not the determining factor. J Am Chem Soc 2001;123:7907–7908. - PubMed
-
- Gillig KJ, Ruotolo BT, Stone EG, et al. Coupling high-pressure MALDI with ion mobility/orthogonal time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 2000;72:3965–3971. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
