The use of real-time reverse transcriptase PCR for the quantification of cytokine gene expression
- PMID: 12901609
- PMCID: PMC2279895
The use of real-time reverse transcriptase PCR for the quantification of cytokine gene expression
Abstract
Real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is becoming a widely used method to quantify cytokines from cells, tissues, or tissue biopsies. The method allows for the direct detection of PCR product during the exponential phase of the reaction, combining amplification and detection in a single step. Using TaqMan chemistry (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) and the ABI Prism 7700 Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems), we validated a large panel of murine and human cytokines, as we as other factors playing a role in the immune system, such a chemokines and apoptotic markers. Although the method allows fast, sensitive, and accurate quantification, different control assays are necessary for the method to be reliable. By construction of complementary DNA (cDNA) plasmid clones, standard curves are generated that allow direct quantification of every unknown sample. Furthermore, the choice of a reliable housekeeping gene is very important. Finally, co-amplification of contaminating genomic DNA is avoided by designing sets of primers located in different exons or or intron-exon junctions. In conclusion, the real-time RT-PCF technique is very accurate and sensitive, allows high through put, and can be performed on very small samples. The development of real-time RT-PCR has resulted in an exponential increase in its use over the last couple of years, and the method has undoubtedly become the standard for quantifying cytokine patterns, clarifying many functional properties of immune cells and their associated diseases.
Figures

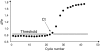
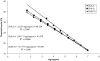
References
-
- Li A, Forestier E, Rosenquist R, Roos G. Minimal residual disease quantification in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia by real-time polymerase chain reaction using the SYBR Green dye. Exp Hematol 2002;30:1170–1177. - PubMed
-
- Bernard PS, Wittwer CT. Real-time PCR technology for cancer diagnostics. Clin Chem 2002;48:1178–1185. - PubMed
-
- Norton DM. Polymerase chain reaction-based methods for detection of Listeria monocytogenes: toward real-time screening for food and environmental samples. J AOAC Int 2002;85:505–515. - PubMed
-
- Niesters HG. Quantitation of viral load using real-time amplification techniques. Methods 2001;25:419–429. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed FE. Detection of genetically modified organisms in foods. Trends Biotechnol 2002;20:215–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
