Production and properties of bacteriocin-like inhibitory substances from the swine pathogen Streptococcus suis serotype 2
- PMID: 12902232
- PMCID: PMC169146
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.8.4482-4488.2003
Production and properties of bacteriocin-like inhibitory substances from the swine pathogen Streptococcus suis serotype 2
Abstract
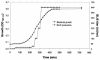
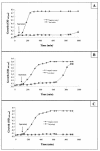
Streptococcus suis serotype 2 is a major pathogen found in the upper respiratory tract of swine. In this study, isolates of this bacterial species were tested for the production of bacteriocin-like inhibitory substances (BLIS). Of the 38 strains tested, four inhibited the growth of other S. suis isolates according to a deferred-antagonism plate assay. Interestingly, three of the strains were originally isolated from healthy carrier pigs and were considered nonvirulent. Three isolates (94-623, 90-1330, and AAH4) that produced BLIS in liquid broth were selected for further characterization. None of the inhibitory activities was related to the production of either organic acids or hydrogen peroxide. The BLIS produced by these strains were heat stable and proteinase K, pronase, and elastase sensitive but were trypsin and chymotrypsin resistant. They were stable at pH 2 and 12 and had molecular masses in the range of 14 to 30 kDa. Maximum production was observed during the mid-log phase. Following a curing procedure with novobiocin, only 90-1330 lost the ability to produce BLIS, suggesting that the BLIS might be plasmid encoded. Analysis of the inhibitory spectra revealed that the BLIS-producing strains also inhibited the growth of Actinobacillus minor, Actinobacillus porcinus, Enterococcus durans, Micrococcus luteus, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. dysgalactiae, Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus, and S. dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis. This study reports for the first time the ability of the swine pathogen S. suis serotype 2 to produce BLIS with the characteristics of classic bacteriocins. Further studies are required to investigate the possibility of using bacteriocin-producing strains to prevent swine infections caused by virulent strains of S. suis serotype 2.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Purification and Characterization of Suicin 65, a Novel Class I Type B Lantibiotic Produced by Streptococcus suis.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 28;10(12):e0145854. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145854. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26709705 Free PMC article.
-
Suicin 90-1330 from a nonvirulent strain of Streptococcus suis: a nisin-related lantibiotic active on gram-positive swine pathogens.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014 Sep;80(17):5484-92. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01055-14. Epub 2014 Jun 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24973067 Free PMC article.
-
Suicin 3908, a new lantibiotic produced by a strain of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 isolated from a healthy carrier pig.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 6;10(2):e0117245. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117245. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25659110 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriocin Production by Beta-Hemolytic Streptococci.Pathogens. 2021 Jul 9;10(7):867. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10070867. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34358017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacteriocin as weapons in the marine animal-associated bacteria warfare: inventory and potential applications as an aquaculture probiotic.Mar Drugs. 2010 Apr 4;8(4):1153-77. doi: 10.3390/md8041153. Mar Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20479972 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential of cell-free supernatants from cultures of selected lactic acid bacteria and yeast obtained from local fermented foods as inhibitors of Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella spp. and Staphylococcus aureus.BMC Res Notes. 2014 Sep 4;7:606. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-606. BMC Res Notes. 2014. PMID: 25190588 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and Characterization of Suicin 65, a Novel Class I Type B Lantibiotic Produced by Streptococcus suis.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 28;10(12):e0145854. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145854. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26709705 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effect between two bacteriocin-like inhibitory substances produced by Lactobacilli Strains with inhibitory activity for Streptococcus agalactiae.Curr Microbiol. 2012 Apr;64(4):349-56. doi: 10.1007/s00284-011-0077-0. Epub 2012 Jan 10. Curr Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22231454
-
Protease-Sensitive Inhibitory Activity of Cell-free Supernatant of Lactobacillus crispatus 156 Synergizes with Ciprofloxacin, Moxifloxacin and Streptomycin Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An In Vitro Study.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2015 Jun;7(2):172-80. doi: 10.1007/s12602-015-9188-4. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2015. PMID: 25693845
-
Suicin 90-1330 from a nonvirulent strain of Streptococcus suis: a nisin-related lantibiotic active on gram-positive swine pathogens.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014 Sep;80(17):5484-92. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01055-14. Epub 2014 Jun 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24973067 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aarestrup, F. M., S. R. Rasmussen, K. Artursson, and N. E. Jensen. 1998. Trends in the resistance to antimicrobial agents of Streptococcus suis isolates from Denmark and Sweden. Vet. Microbiol. 63:71-80. - PubMed
-
- Baele, M., K. Chiers, L. A. Devriese, H. E. Smith, H. J. Wisselink, M. Vaneechoutte, and F. Haesebrouck. 2001. The gram-positive tonsillar and nasal flora of piglets before and after weaning. J. Appl. Microbiol. 91:997-1003. - PubMed
-
- Brook, I. 1999. Bacterial interference. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 25:155-172. - PubMed
-
- Cantin, M., J. Harel, R. Higgins, and M. Gottschalk. 1992. Antimicrobial resistance patterns and plasmid profiles of Streptococcus suis isolates. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 4:170-174. - PubMed
-
- Cintas, L. M., M. P. Casaus, C. Herranz, I. F. Nes, and P. E. Hernandez. 2001. Review: bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria. Food Sci. Tech. Int. 7:281-305.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

