Engineering Deinococcus geothermalis for bioremediation of high-temperature radioactive waste environments
- PMID: 12902245
- PMCID: PMC169113
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.8.4575-4582.2003
Engineering Deinococcus geothermalis for bioremediation of high-temperature radioactive waste environments
Abstract
Deinococcus geothermalis is an extremely radiation-resistant thermophilic bacterium closely related to the mesophile Deinococcus radiodurans, which is being engineered for in situ bioremediation of radioactive wastes. We report that D. geothermalis is transformable with plasmids designed for D. radiodurans and have generated a Hg(II)-resistant D. geothermalis strain capable of reducing Hg(II) at elevated temperatures and in the presence of 50 Gy/h. Additionally, D. geothermalis is capable of reducing Fe(III)-nitrilotriacetic acid, U(VI), and Cr(VI). These characteristics support the prospective development of this thermophilic radiophile for bioremediation of radioactive mixed waste environments with temperatures as high as 55 degrees C.
Figures
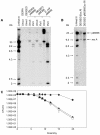
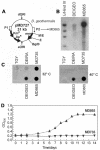
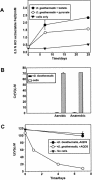
References
-
- Agnew, S. F., and R. A. Corbin. 1998. Analysis of SX farm leak histories: historical leak model. Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, N.Mex.
-
- Arnone, M. I., L. Birolo, M. V. Cubellis, G. Nitti, G. Marino, and G. Sannia. 1992. Expression of a hyperthermophilic aspartate aminotransferase in Escherichia coli. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1160:206-212. - PubMed
-
- Barrineau, P., P. Gilbert, W. J. Jackson, C. S. Jones, A. O. Summers, and S. Wisdom. 1985. The structure of the mer operon. Basic Life Sci. 30:707-718. - PubMed
-
- Battista, J. R. 1997. Against all odds: the survival strategies of Deinococcus radiodurans. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 51:203-224. - PubMed
-
- Brim, H., S. C. McFarlan, J. K. Fredrickson, K. W. Minton, M. Zhai, L. P. Wackett, and M. J. Daly. 2000. Engineering Deinococcus radiodurans for metal remediation in radioactive mixed waste environments. Nat. Biotechnol. 18:85-90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

