Effects of essential oils on ruminal microorganisms and their protein metabolism
- PMID: 12902303
- PMCID: PMC169102
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.8.5011-5014.2003
Effects of essential oils on ruminal microorganisms and their protein metabolism
Abstract
A commercial blend of essential oil (EO) compounds was added to a grass, maize silage, and concentrate diet fed to dairy cattle in order to determine their influence on protein metabolism by ruminal microorganisms. EO inhibited (P < 0.05) the rate of deamination of amino acids. Pure-culture studies indicated that the species most sensitive to EO were ammonia-hyperproducing bacteria and anaerobic fungi.
Figures
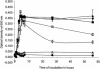
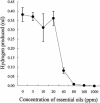
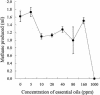
References
-
- Eschenlauer, S. C. P., N. McKain, N. D. Walker, N. R. McEwan, C. J. Newbold, and R. J. Wallace. 2002. Ammonia production by rumen microorganisms and enumeration, isolation, and characterization of bacteria capable of growth on peptides and amino acids from the sheep rumen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68:4925-4931. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

