Proteasome inhibitors disrupt the unfolded protein response in myeloma cells
- PMID: 12902539
- PMCID: PMC187896
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1334037100
Proteasome inhibitors disrupt the unfolded protein response in myeloma cells
Abstract
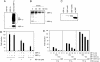
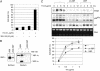
Novel agents that target the proteasome, a proteolytic complex responsible for the degradation of ubiquitinated proteins, have demonstrated remarkable therapeutic efficacy in multiple myeloma, a plasma cell malignancy. However, the mechanism by which these compounds act remains unknown. A signaling pathway called the unfolded protein response (UPR) allows cells to handle the proper folding of proteins. The transcription factor XBP-1, a regulator of the UPR, is also required for plasma cell differentiation, suggesting a link between the UPR and plasma cell differentiation. Here we show that proteasome inhibitors target XBP-1 and the UPR in myeloma cells. Proteasome inhibitors suppress the activity of the translumenal endoplasmic reticulum endoribonuclease/kinase, IRE1 alpha, to impair the generation of the active, spliced XBP-1 species and simultaneously stabilize the unspliced species that acts as a dominant negative. Myeloma cells rendered functionally deficient in XBP-1 undergo increased apoptosis in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Identification of compounds that target the activity of IRE1 alpha/XBP-1 may yield novel therapies for the treatment of multiple myeloma and other malignancies that rely on an intact UPR.
Figures


References
-
- Orlowski, R. Z., Stinchcombe, T. E., Mitchell, B. S., Shea, T. C., Baldwin, A. S., Stahl, S., Adams, J., Esseltine, D. L., Elliott, P. J., Pien, C. S., et al. (2002) J. Clin. Oncol. 20, 4420–4427. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, K. C. (2002) Semin. Oncol. 29, 17–20. - PubMed
-
- Barlogie, B., Shaughnessy, J., Zangari, M. & Tricot, G. (2002) Semin. Oncol. 29, 26–33. - PubMed
-
- Adams, J. (2002) Curr. Opin. Oncol. 14, 628–634. - PubMed
-
- Kisselev, A. F. & Goldberg, A. L. (2001) Chem. Biol. 8, 739–758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

