MicroRNAs and small interfering RNAs can inhibit mRNA expression by similar mechanisms
- PMID: 12902540
- PMCID: PMC187842
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1630797100
MicroRNAs and small interfering RNAs can inhibit mRNA expression by similar mechanisms
Abstract
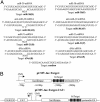
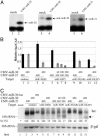
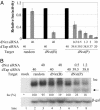
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenously encoded small noncoding RNAs, derived by processing of short RNA hairpins, that can inhibit the translation of mRNAs bearing partially complementary target sequences. In contrast, small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), which are derived by processing of long double-stranded RNAs and are often of exogenous origin, degrade mRNAs bearing fully complementary sequences. Here, we demonstrate that an endogenously encoded human miRNA is able to cleave an mRNA bearing fully complementary target sites, whereas an exogenously supplied siRNA can inhibit the expression of an mRNA bearing partially complementary sequences without inducing detectable RNA cleavage. These data suggest that miRNAs and siRNAs can use similar mechanisms to repress mRNA expression and that the choice of mechanism may be largely or entirely determined by the degree of complementary of the RNA target.
Figures


References
-
- Hutvágner, G. & Zamore, P. D. (2002) Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 12, 225–232. - PubMed
-
- Cullen, B. R. (2002) Nat. Immunol. 3, 597–599. - PubMed
-
- Hammond, S. M., Bernstein, E., Beach, D. & Hannon, G. J. (2000) Nature 404, 293–295. - PubMed
-
- Zamore, P. D., Tuschl, T., Sharp, P. A. & Bartel, D. P. (2000) Cell 101, 25–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

