Single-molecule study of DNA unlinking by eukaryotic and prokaryotic type-II topoisomerases
- PMID: 12902541
- PMCID: PMC187850
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1631550100
Single-molecule study of DNA unlinking by eukaryotic and prokaryotic type-II topoisomerases
Abstract
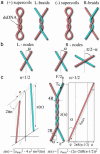
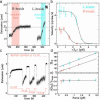
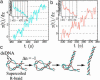
Type-II topoisomerases are responsible for untangling DNA during replication by removing supercoiled and interlinked DNA structures. Using a single-molecule micromanipulation setup, we follow the real-time decatenation of two mechanically braided DNA molecules by Drosophila melanogaster topoisomerase (Topo) II and Escherichia coli Topo IV. Although Topo II relaxes left-handed (L) and right-handed (R-) braids similarly at a rate of approximately 2.9 s-1, Topo IV has a marked preference for L-braids, which it relaxes completely and processively at a rate of approximately 2.4 s-1. However, Topo IV can unlink R-braids at about half that rate when they supercoil to form L-plectonemes. These results imply that the preferred substrate for unlinking by Topo IV has the symmetry of an L-crossing and shed new light on the decatenation of daughter strands during DNA replication, which are usually assumed to be linked in an R-braid.
Figures


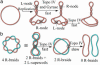
Similar articles
-
Chirality sensing by Escherichia coli topoisomerase IV and the mechanism of type II topoisomerases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jul 22;100(15):8654-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1133178100. Epub 2003 Jul 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12857958 Free PMC article.
-
Single-molecule analysis of DNA uncoiling by a type II topoisomerase.Nature. 2000 Apr 20;404(6780):901-4. doi: 10.1038/35009144. Nature. 2000. PMID: 10786800
-
The interaction of Escherichia coli topoisomerase IV with DNA.J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 20;270(42):25286-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.42.25286. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7559669
-
[DNA supercoiling and topoisomerases in Escherichia coli].Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 1995 Jul-Sep;37(3):291-304. Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8850348 Review. Spanish.
-
DNA topoisomerases: nature's solution to the topological ramifications of the double-helix structure of DNA.Harvey Lect. 1985-1986;81:93-110. Harvey Lect. 1985. PMID: 2833466 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
DNA supercoiling in bacteria: state of play and challenges from a viewpoint of physics based modeling.Front Microbiol. 2023 Oct 30;14:1192831. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1192831. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37965550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome maintenance in the context of 4D chromatin condensation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Aug;73(16):3137-50. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2221-2. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27098512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromatin Architectural Factors as Safeguards against Excessive Supercoiling during DNA Replication.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 24;21(12):4504. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124504. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32599919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromatinization modulates topoisomerase II processivity.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 27;14(1):6844. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42600-z. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37891161 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into the Geometry and Topology of DNA Replication Intermediates.Biology (Basel). 2025 Apr 26;14(5):478. doi: 10.3390/biology14050478. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427666 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

