Evidence for genetic linkage between the gene segments encoding NSP4 and VP6 proteins in common and reassortant human rotavirus strains
- PMID: 12904356
- PMCID: PMC179808
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.8.3566-3573.2003
Evidence for genetic linkage between the gene segments encoding NSP4 and VP6 proteins in common and reassortant human rotavirus strains
Abstract
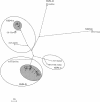
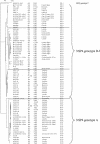
NSP4-encoding genes of 78 human rotavirus strains of common or reassortant genotypes were characterized by reverse transcription-PCR followed by sequencing and phylogenetic analysis. It was found that all the human strains characterized clustered into only two of the five known NSP4 genotypes. Linkage between NSP4 genotypes and VP6 subgroups was 100%, NSP4 genotype A being linked to VP6 of subgroup I (SGI) and NSP4 of genotype B being linked to VP6 of SGII. The diversity among the NSP4- and VP6-encoding genes was significantly less than that among the VP7 and VP4 genes in cocirculating human rotavirus strains. Whereas G and P types appear to be shared among different animal species and humans, the NSP4- and VP6-encoding genes appear to segregate according to their host of origin, suggesting that these two proteins may be host restriction determinants. The NSP4-VP6 association may be structurally determined during rotavirus replication (morphogenesis).
Figures


References
-
- Au, K. S., N. M. Mattion, and M. K. Estes. 1993. A subviral particle binding domain on the rotavirus nonstructural glycoprotein NS28. Virology 194:665-673. - PubMed
-
- Ball, J. M., P. Tian, C. Q. Zeng, A. P. Morris, and M. K. Estes. 1996. Age-dependent diarrhea induced by a rotaviral nonstructural glycoprotein. Science 272:101-104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

