Comparative evaluation of real-time PCR assays for detection of the human metapneumovirus
- PMID: 12904367
- PMCID: PMC179772
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.8.3631-3635.2003
Comparative evaluation of real-time PCR assays for detection of the human metapneumovirus
Abstract
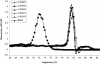
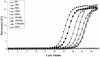
The human metapneumovirus (hMPV) is a new member of the Paramyxoviridae family associated with acute respiratory tract infections in humans. The objective of this study was to compare the sensitivity of real-time RT-PCR assays performed in a LightCycler instrument and designed to amplify the viral nucleoprotein (N), matrix (M), fusion (F), phosphoprotein (P), and polymerase (L) genes. In a first evaluation of 20 viral cultures with characteristics compatible with hMPV cytopathic effect, the PCR positivity rates were 100, 90, 75, 60, and 55% using primers for the N, L, M, P, and F genes. In a second evaluation of 10 nasopharyngeal aspirates from children with bronchiolitis and found to be positive for the hMPV N gene, the PCR positivity rates for the L, M, P, and F genes were 90, 60, 30, and 80%, respectively. The analytic sensitivity of the real-time RT-PCR assay for the hMPV N gene was 100 copies using a transcribed viral plasmid. In conclusion, real-time PCR assays aimed at amplifying the N and L genes which are coding for two internal viral proteins appear particularly suitable for hMPV diagnostic.
Figures
References
-
- Boivin, G., Y. Abed, G. Pelletier, L. Ruel, D. Moisan, S. Côté, T. Peret, D. Erdman, and L. Anderson. 2002. Virological features and clinical manifestations associated with the human metapneumovirus, a new paramyxovirus responsible for acute respiratory tract infections in all age groups. J. Infect. Dis. 186:1330-1334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

