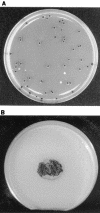
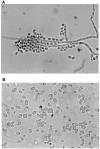
Identification of Exophiala mesophila isolated from treated dental unit waterlines
- PMID: 12904410
- PMCID: PMC179780
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.8.3885-3889.2003
Identification of Exophiala mesophila isolated from treated dental unit waterlines
Abstract
Members of the genus Exophiala are often difficult to identify to the species level because of their variable morphological appearances. This paper describes the methods used to identify Exophiala mesophila and provides salient differential features for distinguishing other mesophilic members of the genus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exophiala mesophila spec. nov.Mycoses. 1996 Jan-Feb;39(1-2):1-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1996.tb00076.x. Mycoses. 1996. PMID: 8786751
-
Spectrum of clinically relevant Exophiala species in the United States.J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Nov;45(11):3713-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02012-06. Epub 2007 Jun 27. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17596364 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of an unusual fungus in treated dental unit waterlines.J Am Dent Assoc. 2003 Jul;134(7):853-8. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2003.0283. J Am Dent Assoc. 2003. PMID: 12892442
-
Exophiala spinifera and its allies: diagnostics from morphology to DNA barcoding.Med Mycol. 2008 May;46(3):193-208. doi: 10.1080/13693780701799217. Med Mycol. 2008. PMID: 18404547 Review.
-
Catheter-associated fungemia due to Exophiala oligosperma in a leukemic child and review of fungemia cases caused by Exophiala species.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2006 Nov;25(11):729-32. doi: 10.1007/s10096-006-0205-0. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2006. PMID: 17033790 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Exophiala Species Associated With Disseminated Granulomatous Inflammation in a Captive Eastern Hellbender (Cryptobranchus alleganiensis alleganiensis).Front Vet Sci. 2020 Jan 31;7:25. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00025. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 32083105 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial contamination of dental unit waterlines and effect on quality of indoor air.Environ Monit Assess. 2014 Jun;186(6):3431-44. doi: 10.1007/s10661-014-3628-6. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Environ Monit Assess. 2014. PMID: 24469014
-
In vitro activities of eight antifungal drugs against 106 waterborne and cutaneous exophiala species.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Dec;57(12):6395-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01629-13. Epub 2013 Oct 7. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 24100491 Free PMC article.
-
Culture-Dependent and Amplicon Sequencing Approaches Reveal Diversity and Distribution of Black Fungi in Antarctic Cryptoendolithic Communities.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Mar 16;7(3):213. doi: 10.3390/jof7030213. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33809619 Free PMC article.
-
Mycological contamination in dental unit waterlines in Istanbul, Turkey.Braz J Microbiol. 2014 Jan 15;44(3):977-81. doi: 10.1590/s1517-83822013000300049. eCollection 2013. Braz J Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24516467 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berger, L., and M. Langeron. 1949. Sur un type nouveau de chromomycose observé au Canada (Torula bergeri n. sp.). Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 24:574-599. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1993. Recommended infection control practices for dentistry. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 41:1-12.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2002. Exophiala infection from contaminated injectable steroids prepared by a compounding pharmacy—United States, July-November 2002. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 51:1109-1112. - PubMed
-
- de Hoog, G. S. 1977. Rhinocladiella and allied genera. Stud. Mycol. 15:1-140.
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources