Insulin receptor substrate-2 deficiency impairs brain growth and promotes tau phosphorylation
- PMID: 12904469
- PMCID: PMC6740672
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-18-07084.2003
Insulin receptor substrate-2 deficiency impairs brain growth and promotes tau phosphorylation
Abstract
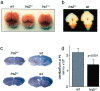
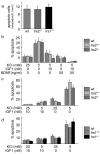
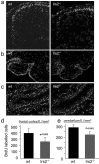
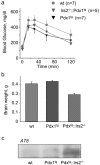
Insulin resistance and diabetes might promote neurodegenerative disease, but a molecular link between these disorders is unknown. Many factors are responsible for brain growth, patterning, and survival, including the insulin-insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-signaling cascades that are mediated by tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate (IRS) proteins. Irs2 signaling mediates peripheral insulin action and pancreatic beta-cell function, and its failure causes diabetes in mice. In this study, we reveal two important roles for Irs2 signaling in the mouse brain. First, disruption of the Irs2 gene reduced neuronal proliferation during development by 50%, which dissociated brain growth from Irs1-dependent body growth. Second, neurofibrillary tangles containing phosphorylated tau accumulated in the hippocampus of old Irs2 knock-out mice, suggesting that Irs2 signaling is neuroprotective. Thus, dysregulation of the Irs2 branch of the insulin-Igf-signaling cascade reveals a molecular link between diabetes and neurodegenerative disease.
Figures



References
-
- Aguirre V, Werner ED, Giraud J, Lee YH, Shoelson SE, White MF ( 2002) Phosphorylation of ser307 in insulin receptor substrate-1 blocks interactions with the insulin receptor and inhibits insulin action. J Biol Chem 277: 1531-1537. - PubMed
-
- Anlar B, Sullivan KA, Feldman EL ( 1999) Insulin-like growth factor-I and central nervous system development. Horm Metab Res 31: 120-125. - PubMed
-
- Bektas A, Warram JH, White MF, Krolewski AS, Doria A ( 1999) Exclusion of insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS-2) as a major locus for early-onset autosomal dominant type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 48: 640-642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
