Nestin expression in hair follicle sheath progenitor cells
- PMID: 12904579
- PMCID: PMC187900
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1733025100
Nestin expression in hair follicle sheath progenitor cells
Abstract
The intermediate filament protein, nestin, marks progenitor cells of the CNS. Such CNS stem cells are selectively labeled by placing GFP under the control of the nestin regulatory sequences. During early anagen or growth phase of the hair follicle, nestin-expressing cells, marked by GFP fluorescence in nestin-GFP transgenic mice, appear in the permanent upper hair follicle immediately below the sebaceous glands in the follicle bulge. This is where stem cells for the hair follicle outer-root sheath are thought to be located. The relatively small, oval-shaped, nestin-expressing cells in the bulge area surround the hair shaft and are interconnected by short dendrites. The precise locations of the nestin-expressing cells in the hair follicle vary with the hair cycle. During telogen or resting phase and in early anagen, the GFP-positive cells are mainly in the bulge area. However, in mid- and late anagen, the GFP-expressing cells are located in the upper outer-root sheath as well as in the bulge area but not in the hair matrix bulb. These observations show that the nestin-expressing cells form the outer-root sheath. Results of the immunohistochemical staining showed that nestin, GFP, keratin 5/8, and keratin 15 colocalize in the hair follicle bulge cells, outer-root sheath cells, and basal cells of the sebaceous glands. These data indicate that nestin-expressing cells, marked by GFP, in the hair follicle bulge are indeed progenitors of the follicle outer-root sheath. The expression of the unique protein, nestin, in both neural stem cells and hair follicle stem cells suggests their possible relation.
Figures
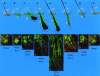

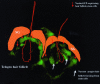
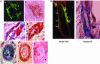
References
-
- Oshima, H., Rochat, A., Kedzia, C., Kobayashi, K. & Barrandon, Y. (2001) Cell 104, 233–245. - PubMed
-
- Cotsarelis, G., Sun, T.-T. & Lavker, R. M. (1990) Cell 61, 1329–1337. - PubMed
-
- Taylor, G., Lehrer, M. S., Jensen, P. J., Sun, T.-T. & Lavker, R. M. (2000) Cell 102, 451–461. - PubMed
-
- Toma, J. G., Akhavan, M., Fernandes, J. L., Barnabe-Heider, F., Sadikot, A., Kaplan, D. R. & Miller, F. D. (2001) Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 778–784. - PubMed
-
- Lendahl, U., Zimmerman, L. B. & McKay, R. D. G. (1990) Cell 60, 585–595. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

