HTLV-1 Rex is required for viral spread and persistence in vivo but is dispensable for cellular immortalization in vitro
- PMID: 12907436
- PMCID: PMC2852248
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2003-05-1490
HTLV-1 Rex is required for viral spread and persistence in vivo but is dispensable for cellular immortalization in vitro
Abstract
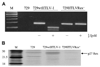
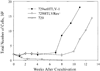
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is associated with leukemia/lymphoma and neurologic disorders. Although the viral transcriptional activator Tax is the critical viral oncoprotein, Rex, which regulates the expression of the viral structural and enzymatic genes, is essential for efficient viral replication. Herein, we investigate the contribution of Rex in HTLV-1 immortalization of primary T cells in vitro and viral survival in an infectious rabbit animal model. A Rex-deficient HTLV-1 (HTLVRex-) was constructed and characterized for viral gene expression, protein production, and immortalization capacity. Cells transiently transfected with the HTLVRex- proviral clone produced low detectable levels of p19 Gag. 729HTLVRex- stable transfectants produced functional Tax, but undetectable levels of Rex or p19 Gag. Coculture of irradiated 729HTLVRex- cells with peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) resulted in sustained interleukin-2 (IL-2)-dependent growth of primary T lymphocytes. These cells carried the HTLVRex- genome and expressed tax/rex mRNA but produced no detectable Rex or p19 Gag. Rabbits inoculated with irradiated 729HTLVRex- cells or 729HTLVRex- cells transiently transfected with a Rex cDNA expression plasmid failed to become persistently infected or mount a detectable antibody response to the viral gene products. Together, our results provide the first direct evidence that Rex and its function to modulate viral gene expression and virion production is not required for in vitro immortalization by HTLV-1. However, Rex is critical for efficient infection of cells and persistence in vivo.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Tax and overlapping rex sequences do not confer the distinct transformation tropisms of human T-cell leukemia virus types 1 and 2.J Virol. 2003 Jul;77(14):7728-35. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.14.7728-7735.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12829812 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 expressing nonoverlapping tax and rex genes replicates and immortalizes primary human T lymphocytes but fails to replicate and persist in vivo.J Virol. 2005 Dec;79(23):14473-81. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.23.14473-14481.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16282446 Free PMC article.
-
The human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Rex regulatory protein exhibits an impaired functionality in human lymphoblastoid Jurkat T cells.J Virol. 1997 Nov;71(11):8514-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.11.8514-8521.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9343209 Free PMC article.
-
[The role of region pX in the life cycle of HTLV-I and in carcinogenesis].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2003 May-Jun;37(3):392-403. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2003. PMID: 12815946 Review. Russian.
-
Mechanisms of HTLV-1 persistence and transformation.Br J Cancer. 2009 Nov 3;101(9):1497-501. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605345. Epub 2009 Sep 29. Br J Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19861996 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Tax protein in human T-cell leukemia virus type-I leukemogenicity.Retrovirology. 2004 Aug 13;1:20. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-1-20. Retrovirology. 2004. PMID: 15310405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Past, Present, and Future of a Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 Vaccine.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 4;13:897346. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.897346. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35602078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opticool: Cutting-edge transgenic optical tools.PLoS Genet. 2024 Mar 22;20(3):e1011208. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011208. eCollection 2024 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 38517915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The human T-cell leukemia virus Rex protein.Front Biosci. 2005 Jan 1;10:431-45. doi: 10.2741/1539. Print 2005 Jan 1. Front Biosci. 2005. PMID: 15574380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of the Genetic Organization, Expression Strategies and Oncogenic Potential of HTLV-1 and HTLV-2.Leuk Res Treatment. 2012;2012:876153. doi: 10.1155/2012/876153. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Leuk Res Treatment. 2012. PMID: 23213551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gessain A, Vernant JC, Maurs L, et al. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-1 in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet. 1985;2:407–409. - PubMed
-
- Osame M, Usuku K, Izumo S, et al. HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet. 1986;1:1031–1032. - PubMed
-
- Akagi T, Ono H, Shimotohno K. Expression of cell-cycle regulatory genes in HTLV-I infected T-cell lines: possible involvement of Tax1 in the altered expression of cyclin D2, p18Ink4, and p21Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1. Oncogene. 1996;12:1645–1652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

