Structure-function analysis of the bestrophin family of anion channels
- PMID: 12907679
- PMCID: PMC2885917
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M306150200
Structure-function analysis of the bestrophin family of anion channels
Abstract
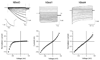
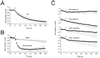
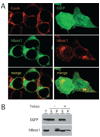
The bestrophins are a newly described family of anion channels unrelated in primary sequence to any previously characterized channel proteins. The human genome codes for four bestrophins, each of which confers a distinctive plasma membrane conductance on transfected 293 cells. Extracellular treatment with methanethiosulfonate ethyltrimethylammonium (MTSET) of a series of substitution mutants that eliminate one or more cysteines from human bestrophin1 demonstrates that cysteine 69 is the single endogenous cysteine responsible for MTSET inhibition of whole-cell current. Cysteines introduced between positions 78-99 and 223-226 are also accessible to external MTSET, with MTSET modification at positions 79, 80, 83, and 90 producing a 2-6-fold increase in whole-cell current. The latter set of four cysteine-substitution mutants define a region that appears to mediate allosteric control of channel activity. Mapping of transmembrane topography by insertion of N-linked glycosylation sites and tobacco etch virus protease cleavage sites provides evidence for cytosolic N and C termini and an unexpected transmembrane topography with at least three extracellular loops that include positions 60-63, 212-227, and 261-267. These experiments provide the first structural analysis of the bestrophin channel family.
Figures





References
-
- Jentsch TJ, Gunther W. BioEssays. 1997;19:117–126. - PubMed
-
- George AL, Bianchi L, Link EM, Vanoye CG. Curr. Biol. 2001;11:R620–R628. - PubMed
-
- Hille B. Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates, Inc.; 2001.
-
- Iyer R, Iverson TM, Accardi A, Miller C. Nature. 2002;419:715–718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

