Repairing the Sickle Cell mutation. II. Effect of psoralen linker length on specificity of formation and yield of third strand-directed photoproducts with the mutant target sequence
- PMID: 12907706
- PMCID: PMC169896
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg659
Repairing the Sickle Cell mutation. II. Effect of psoralen linker length on specificity of formation and yield of third strand-directed photoproducts with the mutant target sequence
Abstract
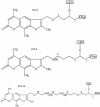
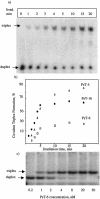
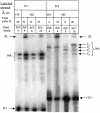
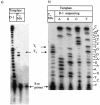
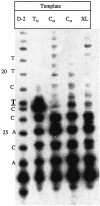
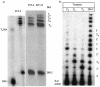
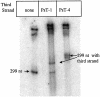
Three identical deoxyoligonucleotide third strands with a 3'-terminal psoralen moiety attached by linkers that differ in length (N = 16, 6 and 4 atoms) and structure were examined for their ability to form triplex-directed psoralen photoproducts with both the mutant T residue of the Sickle Cell beta-globin gene and the comparable wild-type sequence in linear duplex targets. Specificity and yield of UVA (365 nm) and visible (419 nm) light-induced photoadducts were studied. The total photoproduct yield varies with the linker and includes both monoadducts and crosslinks at various available pyrimidine sites. The specificity of photoadduct formation at the desired mutant T residue site was greatly improved by shortening the psoralen linker. In particular, using the N-4 linker, psoralen interaction with the residues of the non-coding duplex strand was essentially eliminated, while modification of the Sickle Cell mutant T residue was maximized. At the same time, the proportion of crosslink formation at the mutant T residue upon UV irradiation was much greater for the N-4 linker. The photoproducts formed with the wild-type target were fully consistent with its single base pair difference. The third strand with the N-4 linker was also shown to bind to a supercoiled plasmid containing the Sickle Cell mutation site, giving photoproduct yields comparable with those observed in the linear mutant target.
Figures

References
-
- Hobbs C.A. and Yoon,K.G. (1994) Differential regulation of gene expression in vivo by triple helix-forming oligonucleotides as detected by a reporter enzyme. Res. Dev., 4, 1–8. - PubMed
-
- Kim H.G., Reddoch,J.F., Mayfield,C., Ebbinghaus,S., Vigneswaran,N., Thomas,S., Jones,D.E. and Miller,D.M. (1998) Inhibition of transcription of the human c-myc protooncogene by intermolecular triplex. Biochemistry, 37, 2299–2304. - PubMed
-
- Giovannangeli C. and Hélène,C. (1997) Progress in developments of triplex-based strategies. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Des., 7, 413–421. - PubMed
-
- Shen L.X., Kandimalla,E.R. and Agrawal,S. (1998) Impact of mixed-backbone oligonucleotides on target binding affinity and target cleaving specificity and selectivity by Escherichia coli RNase H. Bioorg. Med. Chem., 6, 1695–1705. - PubMed
-
- Chan P.P. and Glazer,P.M. (1997) Triplex DNA: fundamentals, advances and potential applications for gene therapy. J. Mol. Med., 75, 267–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

