Efficient incorporation of positively charged 2', 3'-dideoxynucleoside-5'-triphosphates by DNA polymerases and their application in 'direct-load' DNA sequencing
- PMID: 12907718
- PMCID: PMC169923
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg669
Efficient incorporation of positively charged 2', 3'-dideoxynucleoside-5'-triphosphates by DNA polymerases and their application in 'direct-load' DNA sequencing
Abstract
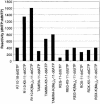
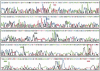
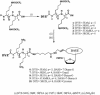
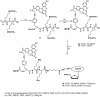
A series of charge-modified, dye-labeled 2', 3'-dideoxynucleoside-5'-triphosphates have been synthesized and evaluated as reagents for dye-terminator DNA sequencing. Unlike the commonly used dye-labeled terminators, these terminators possess a net positive charge and migrate in the opposite direction to dye-labeled Sanger fragments during electrophoresis. Post-sequencing reaction purification is not required to remove unreacted nucleotide or associated breakdown products prior to electrophoresis. Thus, DNA sequencing reaction mixtures can be loaded directly onto a separating medium such as a sequencing gel. The charge-modified nucleotides have also been shown to be more efficiently incorporated by a number of DNA polymerases than regular dye-labeled dideoxynucleotide terminators or indeed normal dideoxynucleoside-5'-triphosphates.
Figures







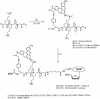
References
-
- International Human Genome Mapping Consortium (2001) A physical map of the human genome. Nature, 409, 934–941. - PubMed
-
- Bergot B.J., Chakerian,V., Connell,C.R., Eadie,J.S., Fung,S., Hershey,N.D., Lee,L.G., Menchen,S.M. and Woo,S.L., (1994) US Patent No. 5 366 860.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

