Cloning, functional analysis and post-transcriptional regulation of a type II DNA topoisomerase from Leishmania infantum. A new potential target for anti-parasite drugs
- PMID: 12907735
- PMCID: PMC169929
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg671
Cloning, functional analysis and post-transcriptional regulation of a type II DNA topoisomerase from Leishmania infantum. A new potential target for anti-parasite drugs
Abstract
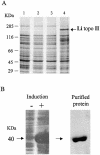
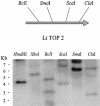
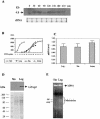
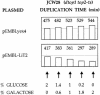
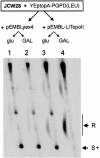
We identified a type II topoisomerase enzyme from Leishmania infantum, a parasite protozoon causing disease in humans. This protein, named Li topo II, which displays a variable C-terminal end, is located in the kinetoplast. The cloned gene encoding Li-TOP2 compensates for the slow growth of topo II-deficient mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, resulting in a catalytically active DNA topoisomerase in yeast. Analysis of the specific mRNA levels of the Li-TOP2 gene showed variations throughout the parasite cell cycle in synchronized cells as well as between the distinct forms of the parasite. Thus, the enzyme had higher levels of mRNA expression in the highly infective intracellular form of the parasite, the amastigote, than in the extracellular promastigote form, suggesting a relation with the distinct developmental and infectious phases of the protozoon. In addition, western blot analysis showed differences in protein expression between the proliferative and non-proliferative forms of L.infantum promastigotes, which displayed similar levels of mRNA. This indicated possible post-transcriptional regulation mechanisms. The data suggest that Li topo II has a part in DNA decatenation and probably at the initial stages of proliferation in the intracellular form of L.infantum, a parasite that has to proliferate into the host macrophage to survive its hostile environment in its first moments of intracellular infection.
Figures




References
-
- Neva F. and Sacks,S. (1995) Leishmaniasis. In Warren,K.S. and Mahmoud,A.A.S. (eds), Leishmaniasis in Tropical and Geographical Medicine. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp. 296–308.
-
- Jimenez M.I., Gutierrez-Solar,B., Benito,A., Aguiar,A., García,E., Carcenado,E. and Alvar,J. (1991) Cutaneous Leishmania infantum zymodems isolated from bone marrow in AIDS patients. Res. Rev. Parasitol., 51, 91–95.
-
- Sacks D.L. and Perkins,P.V. (1984) Identification of an infective stage of Leishmania promastigotes. Science, 223, 1417–1419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

