High concentrations of long interspersed nuclear element sequence distinguish monoallelically expressed genes
- PMID: 12909712
- PMCID: PMC187893
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1737401100
High concentrations of long interspersed nuclear element sequence distinguish monoallelically expressed genes
Abstract
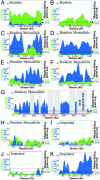
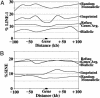
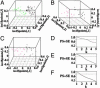
Genes subject to monoallelic expression are expressed from only one of the two alleles either selected at random (random monoallelic genes) or in a parent-of-origin specific manner (imprinted genes). Because high densities of long interspersed nuclear element (LINE)-1 transposon sequence have been implicated in X-inactivation, we asked whether monoallelically expressed autosomal genes are also flanked by high densities of LINE-1 sequence. A statistical analysis of repeat content in the regions surrounding monoallelically and biallelically expressed genes revealed that random monoallelic genes were flanked by significantly higher densities of LINE-1 sequence, evolutionarily more recent and less truncated LINE-1 elements, fewer CpG islands, and fewer base-pairs of short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) sequence than biallelically expressed genes. Random monoallelic and imprinted genes were pooled and subjected to a clustering analysis algorithm, which found two clusters on the basis of aforementioned sequence characteristics. Interestingly, these clusters did not follow the random monoallelic vs. imprinted classifications. We infer that chromosomal sequence context plays a role in monoallelic gene expression and may involve the recognition of long repeats or other features. The sequence characteristics that distinguished the high-LINE-1 category were used to identify more than 1,000 additional genes from the human and mouse genomes as candidate genes for monoallelic expression.
Figures

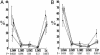
References
-
- Nicholls, R. D. & Knepper, J. L. (2001) Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2, 153–175. - PubMed
-
- Lyon, M. F. (1961) Nature 190, 372–373. - PubMed
-
- Riggs, A. D. (1990) Aust. J. Zool. 37, 419–441.
-
- Gartler, S. M. & Riggs, A. D. (1983) Annu. Rev. Genet. 17, 155–190. - PubMed
-
- Lyon, M. F. (1998) Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 80, 133–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

