The 15-lipoxygenase-1 product 13-S-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid down-regulates PPAR-delta to induce apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells
- PMID: 12909723
- PMCID: PMC187904
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1631086100
The 15-lipoxygenase-1 product 13-S-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid down-regulates PPAR-delta to induce apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells
Abstract
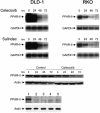
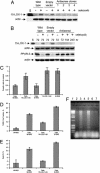
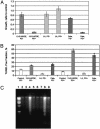
Diminished apoptosis, a critical event in tumorigenesis, is linked to down-regulated 15-lipoxygenase-1 (15-LOX-1) expression in colorectal cancer cells. 13-S-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid (13-S-HODE), which is the primary product of 15-LOX-1 metabolism of linoleic acid, restores apoptosis. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) transcriptionally up-regulate 15-LOX-1 expression to induce apoptosis. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) are nuclear receptors for linoleic and arachidonic acid metabolites. PPAR-delta promotes colonic tumorigenesis. NSAIDs suppress PPAR-delta activity in colon cancer cells. The mechanistic relationship between 15-LOX-1 and PPAR-delta was previously unknown. Our current study shows that (i) 13-S-HODE binds to PPAR-delta, decreases PPAR-delta activation, and down-regulates PPAR-delta expression in colorectal cancer cells; (ii) the induction of 15-LOX-1 expression is a critical step in NSAID down-regulation of PPAR-delta and the resultant induction of apoptosis; and (iii) PPAR-delta is an important signaling receptor for 13-S-HODE-induced apoptosis. The in vivo relevance of these mechanistic findings was demonstrated in our tumorigenesis studies in nude mouse xenograft models. Our findings indicate that the down-regulation of PPAR-delta by 15-LOX-1 through 13-S-HODE is an apoptotic signaling pathway that is activated by NSAIDs.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

