Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) released from Helicobacter pylori stimulated gastric epithelial cells induces cyclooxygenase 2 expression and activation in T cells
- PMID: 12912855
- PMCID: PMC1773780
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.52.9.1257
Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) released from Helicobacter pylori stimulated gastric epithelial cells induces cyclooxygenase 2 expression and activation in T cells
Abstract
Background: and aims: To clarify the interaction between gastric epithelial and mucosal T cells, we examined the role of cytokines released from epithelial cells in response to Helicobacter pylori water extract protein (HPWEP) in regulating T cell cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) expression and activation.
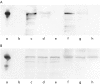
Methods: Media from MKN-28 cells incubated with HPWEP for 48 hours were added to Jurkat T cells and human peripheral T cells. C-C and CXC chemokine concentrations in MKN-28 cell media, and COX-2 expression, interferon gamma (IFN-gamma), and interleukin (IL)-4 secretions in T cells were determined by western blot analysis and ELISA methods. Distributions of COX-2 positive T cells and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) in tissue specimens with H pylori associated gastritis were determined as single or double labelling by immunohistochemistry.
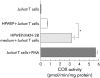
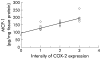
Results: MCP-1, IL-7, IL-8, and RANTES were detected in media from MKN-28 cells incubated with HPWEP. Media as a whole, and MCP-1 alone, stimulated COX-2 expression and peripheral T cell proliferation. Anti-MCP-1 antibody inhibited media stimulated COX-2 mRNA expression in Jurkat T cells. Media stimulated IFN-gamma but not IL-4 secretion from peripheral T cells, while MCP-1 stimulated IL-4 but not IFN-gamma secretion. Both stimulated cytokine release, and peripheral T cell proliferation was partially inhibited by NS-398, a specific COX-2 inhibitor. In mucosa with gastritis, COX-2 was expressed in T cells and MCP-1 was localised mainly in epithelial and mononuclear cells. MCP-1 levels and the intensity of COX-2 expression in tissue samples were closely related.
Conclusions: Cytokines such as MCP-1, released from gastric epithelial cells in response to HPWEP, seem to modulate T cell immune responses, at least in part via COX-2 expression.
Figures





References
-
- Keates S, Sougioultzis S, Keates AC, et al. Cag+ Helicobacter pylori induce transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in AGS gastric epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 2001;276:48127–34. - PubMed
-
- Crowe SE, Alvarez L, Dytoc M, et al. Expression of interleukin 8 and CD 54 by human gastric epithelium after Helicobacter pylori infection in vitro. Gastroenterology 1995;108:65–74. - PubMed
-
- D’Elios MM, Manghetti M, Carli MD, et al. T helper 1 effector cells specific for Helicobacter pylori in the gastric antrum of patients with peptic ulcer disease. J Immunol 1997;158:962–7. - PubMed
-
- Abe N, Katamura K, Shintaku N, et al. Prostaglandin E2 and IL-4 provide native CD4+ T cells with distinct inhibitory signals for the priming of IFN-γ production. Cell Immunol 1997;181:86–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
