Diverse sequences within Tlr elements target programmed DNA elimination in Tetrahymena thermophila
- PMID: 12912887
- PMCID: PMC178349
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.2.4.678-689.2003
Diverse sequences within Tlr elements target programmed DNA elimination in Tetrahymena thermophila
Abstract
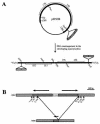
Tlr elements are a novel family of approximately 30 putative mobile genetic elements that are confined to the germ line micronuclear genome in Tetrahymena thermophila. Thousands of diverse germ line-limited sequences, including the Tlr elements, are specifically eliminated from the differentiating somatic macronucleus. Macronucleus-retained sequences flanking deleted regions are known to contain cis-acting signals that delineate elimination boundaries. It is unclear whether sequences within deleted DNA also play a regulatory role in the elimination process. In the current study, an in vivo DNA rearrangement assay was used to identify internal sequences required in cis for the elimination of Tlr elements. Multiple, nonoverlapping regions from the approximately 23-kb Tlr elements were independently sufficient to stimulate developmentally regulated DNA elimination when placed within the context of flanking sequences from the most thoroughly characterized family member, Tlr1. Replacement of element DNA with macronuclear or foreign DNA abolished elimination activity. Thus, diverse sequences dispersed throughout Tlr DNA contain cis-acting signals that target these elements for programmed elimination. Surprisingly, Tlr DNA was also efficiently deleted when Tlr1 flanking sequences were replaced with DNA from a region of the genome that is not normally associated with rearrangement, suggesting that specific flanking sequences are not required for the elimination of Tlr element DNA.
Figures
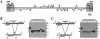





Similar articles
-
Role of micronucleus-limited DNA in programmed deletion of mse2.9 during macronuclear development of Tetrahymena thermophila.Eukaryot Cell. 2004 Apr;3(2):288-301. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.2.288-301.2004. Eukaryot Cell. 2004. PMID: 15075259 Free PMC article.
-
A novel family of mobile genetic elements is limited to the germline genome in Tetrahymena thermophila.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jun 1;30(11):2524-37. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.11.2524. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 12034842 Free PMC article.
-
Flanking regulatory sequences of the Tetrahymena R deletion element determine the boundaries of DNA rearrangement.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Aug;19(8):5631-41. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.8.5631. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10409752 Free PMC article.
-
Whats, hows and whys of programmed DNA elimination in Tetrahymena.Open Biol. 2017 Oct;7(10):170172. doi: 10.1098/rsob.170172. Open Biol. 2017. PMID: 29021213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small RNAs in genome rearrangement in Tetrahymena.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004 Apr;14(2):181-7. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2004.01.004. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004. PMID: 15196465 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of micronucleus-limited DNA in programmed deletion of mse2.9 during macronuclear development of Tetrahymena thermophila.Eukaryot Cell. 2004 Apr;3(2):288-301. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.2.288-301.2004. Eukaryot Cell. 2004. PMID: 15075259 Free PMC article.
-
Developmentally regulated chromosome fragmentation linked to imprecise elimination of repeated sequences in paramecia.Eukaryot Cell. 2003 Oct;2(5):1076-90. doi: 10.1128/EC.2.5.1076-1090.2003. Eukaryot Cell. 2003. PMID: 14555491 Free PMC article.
-
Elimination of foreign DNA during somatic differentiation in Tetrahymena thermophila shows position effect and is dosage dependent.Eukaryot Cell. 2005 Feb;4(2):421-31. doi: 10.1128/EC.4.2.421-431.2005. Eukaryot Cell. 2005. PMID: 15701804 Free PMC article.
-
A non-long terminal repeat retrotransposon family is restricted to the germ line micronucleus of the ciliated protozoan Tetrahymena thermophila.Eukaryot Cell. 2004 Feb;3(1):157-69. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.1.157-169.2004. Eukaryot Cell. 2004. PMID: 14871946 Free PMC article.
-
A Parallel G Quadruplex-Binding Protein Regulates the Boundaries of DNA Elimination Events of Tetrahymena thermophila.PLoS Genet. 2016 Mar 7;12(3):e1005842. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005842. eCollection 2016 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 26950070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannister, A. J., P. Zegerman, J. F. Partridge, E. A. Miska, J. O. Thomas, R. C. Allshire, and T. Kouzarides. 2001. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410:120-124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

