In vivo role of the PIF-binding docking site of PDK1 defined by knock-in mutation
- PMID: 12912918
- PMCID: PMC175797
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg407
In vivo role of the PIF-binding docking site of PDK1 defined by knock-in mutation
Abstract
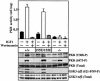
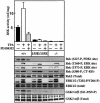
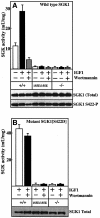
PKB/Akt, S6K, SGK and RSK are mediators of responses triggered by insulin and growth factors and are activated following phosphorylation by 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1). To investigate the importance of a substrate-docking site in the kinase domain of PDK1 termed the 'PIF-pocket', we generated embryonic stem (ES) cells in which both copies of the PDK1 gene were altered by knock-in mutation to express a form of PDK1 retaining catalytic activity, in which the PIF-pocket site was disrupted. The knock-in ES cells were viable, mutant PDK1 was expressed at normal levels and insulin-like growth factor 1 induced normal activation of PKB and phosphorylation of the PKB substrates GSK3 and FKHR. In contrast, S6K, RSK and SGK were not activated, nor were physiological substrates of S6K and RSK phosphorylated. These experiments establish the importance of the PIF-pocket in governing the activation of S6K, RSK, SGK, but not PKB, in vivo. They also illustrate the power of knock-in technology to probe the physiological roles of docking interactions in regulating the specificity of signal transduction pathways.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The in vivo role of PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 binding to PDK1 PH domain defined by knockin mutation.EMBO J. 2004 May 19;23(10):2071-82. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600218. Epub 2004 Apr 29. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15116068 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo role of the phosphate groove of PDK1 defined by knockin mutation.J Cell Sci. 2005 Nov 1;118(Pt 21):5023-34. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02617. Epub 2005 Oct 11. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16219676
-
The PIF-binding pocket in PDK1 is essential for activation of S6K and SGK, but not PKB.EMBO J. 2001 Aug 15;20(16):4380-90. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.16.4380. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11500365 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the role of the 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) signalling pathways.Cell Cycle. 2008 Oct;7(19):2978-82. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.19.6810. Epub 2008 Oct 18. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18802401 Review.
-
Effect of multiple phosphorylation events on the transcription factors FKHR, FKHRL1 and AFX.Biochem Soc Trans. 2002 Aug;30(4):391-7. doi: 10.1042/bst0300391. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002. PMID: 12196101 Review.
Cited by
-
WNK1, the kinase mutated in an inherited high-blood-pressure syndrome, is a novel PKB (protein kinase B)/Akt substrate.Biochem J. 2004 Feb 15;378(Pt 1):257-68. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031692. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 14611643 Free PMC article.
-
The mTOR/PI3K and MAPK pathways converge on eIF4B to control its phosphorylation and activity.EMBO J. 2006 Jun 21;25(12):2781-91. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601166. Epub 2006 Jun 8. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16763566 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 targets protein kinase A in a pathway that regulates interleukin 4.J Exp Med. 2006 Jul 10;203(7):1733-44. doi: 10.1084/jem.20051715. Epub 2006 Jun 19. J Exp Med. 2006. PMID: 16785309 Free PMC article.
-
ATG1, an autophagy regulator, inhibits cell growth by negatively regulating S6 kinase.EMBO Rep. 2007 Apr;8(4):360-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400917. Epub 2007 Mar 9. EMBO Rep. 2007. PMID: 17347671 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into the regulation of PDK1 by phosphoinositides and inositol phosphates.EMBO J. 2004 Oct 13;23(20):3918-28. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600379. Epub 2004 Sep 30. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15457207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi D.R. (2001) Discovery of PDK1, one of the missing links in insulin signal transduction. Biochem. Soc. Trans., 29, 1–14. - PubMed
-
- Avruch J., Belham,C., Weng,Q., Hara,K. and Yonezawa,K. (2001) The p70 S6 kinase integrates nutrient and growth signals to control translational capacity. Prog. Mol. Subcell. Biol., 26, 115–154. - PubMed
-
- Balendran A., Casamayor,A., Deak,M., Paterson,A., Gaffney,P., Currie,R., Downes,C.P. and Alessi,D.R. (1999a) PDK1 acquires PDK2 activity in the presence of a synthetic peptide derived from the carboxyl terminus of PRK2. Curr. Biol., 9, 393–404. - PubMed
-
- Balendran A., Currie,R.A., Armstrong,C.G., Avruch,J. and Alessi,D.R. (1999b) Evidence that PDK1 mediates the phosphorylation of p70 S6 kinase in vivo at Thr412 as well as Thr252. J. Biol. Chem., 274, 37400–37406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

