Elg1 forms an alternative RFC complex important for DNA replication and genome integrity
- PMID: 12912927
- PMCID: PMC175796
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg406
Elg1 forms an alternative RFC complex important for DNA replication and genome integrity
Abstract
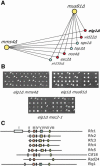
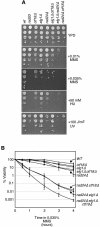
Genome-wide synthetic genetic interaction screens with mutants in the mus81 and mms4 replication fork-processing genes identified a novel replication factor C (RFC) homolog, Elg1, which forms an alternative RFC complex with Rfc2-5. This complex is distinct from the DNA replication RFC, the DNA damage checkpoint RFC and the sister chromatid cohesion RFC. As expected from its genetic interactions, elg1 mutants are sensitive to DNA damage. Elg1 is redundant with Rad24 in the DNA damage response and contributes to activation of the checkpoint kinase Rad53. We find that elg1 mutants display DNA replication defects and genome instability, including increased recombination and mutation frequencies, and minichromosome maintenance defects. Mutants in elg1 show genetic interactions with pathways required for processing of stalled replication forks, and are defective in recovery from DNA damage during S phase. We propose that Elg1-RFC functions both in normal DNA replication and in the DNA damage response.
Figures




References
-
- Aguilera A., Chavez,S. and Malagon,F. (2000) Mitotic recombination in yeast: elements controlling its incidence. Yeast, 16, 731–754. - PubMed
-
- Alcasabas A.A. et al. (2001) Mrc1 transduces signals of DNA replication stress to activate Rad53. Nat. Cell Biol., 3, 958–965. - PubMed
-
- Ayyagari R., Gomes,X.V., Gordenin,D.A. and Burgers,P.M. (2003) Okazaki fragment maturation in yeast. I. Distribution of functions between FEN1 and DNA2. J. Biol. Chem., 278, 1618–1625. - PubMed
-
- Boddy M.N., Gaillard,P.H., McDonald,W.H., Shanahan,P., Yates,J.R.,3rd and Russell,P. (2001) Mus81-Eme1 are essential components of a Holliday junction resolvase. Cell, 107, 537–548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

