DNA polymerase stabilization at stalled replication forks requires Mec1 and the RecQ helicase Sgs1
- PMID: 12912929
- PMCID: PMC175781
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg391
DNA polymerase stabilization at stalled replication forks requires Mec1 and the RecQ helicase Sgs1
Abstract
To ensure proper replication and segregation of the genome, eukaryotic cells have evolved surveillance systems that monitor and react to impaired replication fork progression. In budding yeast, the intra-S phase checkpoint responds to stalled replication forks by downregulating late-firing origins, preventing spindle elongation and allowing efficient resumption of DNA synthesis after recovery from stress. Mutations in this pathway lead to high levels of genomic instability, particularly in the presence of DNA damage. Here we demonstrate by chromatin immunoprecipitation that when yeast replication forks stall due to hydroxyurea (HU) treatment, DNA polymerases alpha and epsilon are stabilized for 40-60 min. This requires the activities of Sgs1, a member of the RecQ family of DNA helicases, and the ATM-related kinase Mec1, but not Rad53 activation. A model is proposed whereby Sgs1 helicase resolves aberrantly paired structures at stalled forks to maintain single-stranded DNA that allows RP-A and Mec1 to promote DNA polymerase association.
Figures
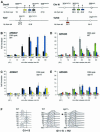
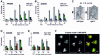
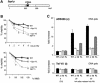
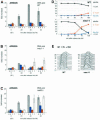

References
-
- Bennett R.J., Sharp,J.A. and Wang,J.C. (1998) Purification and characterization of the Sgs1 DNA helicase activity of S.cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem., 273, 9644–9650. - PubMed
-
- Bjergbaek L., Cobb,J.A. and Gasser,S.M. (2002) RecQ helicases and genome stability: lessons from model organisms and human disease. Swiss Med. Wkly, 132, 433–442. - PubMed
-
- Brosh R.M. Jr, Orren,D.K., Nehlin,J.O., Ravn,P.H., Kenny,M.K., Machwe,A. and Bohr,V.A. (1999) Functional and physical interaction between WRN helicase and human replication protein A. J. Biol. Chem., 274, 18341–18350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

