Expression of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein 70K antisense transcript using APETALA3 promoter suppresses the development of sepals and petals
- PMID: 12913145
- PMCID: PMC181274
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.103.023192
Expression of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein 70K antisense transcript using APETALA3 promoter suppresses the development of sepals and petals
Abstract
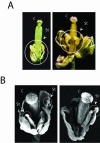
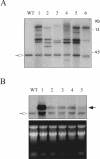
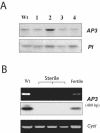
U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP)-70K (U1-70K), a U1 snRNP-specific protein, is involved in the early stages of spliceosome formation. In non-plant systems, it is involved in constitutive and alternative splicing. It has been shown that U1snRNP is dispensable for in vitro splicing of some animal pre-mRNAs, and inactivation of U1-70K in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) is not lethal. As in yeast and humans (Homo sapiens), plant U1-70K is coded by a single gene. In this study, we blocked the expression of Arabidopsis U1-70K in petals and stamens by expressing U1-70K antisense transcript using the AP3 (APETALA3) promoter specific to these floral organs. Flowers of transgenic Arabidopsis plants expressing U1-70K antisense transcript showed partially developed stamens and petals that are arrested at different stages of development. In some transgenic lines, flowers have rudimentary petals and stamens and are male sterile. The severity of the phenotype is correlated with the level of the antisense transcript. Molecular analysis of transgenic plants has confirmed that the observed phenotype is not due to disruption of whorl-specific homeotic genes, AP3 or PISTILLATA, responsible for petal and stamen development. The AP3 transcript was not detected in transgenic flowers with severe phenotype. Flowers of Arabidopsis plants transformed with a reporter gene driven by the same promoter showed no abnormalities. These results show that U1-70K is necessary for the development of sepals and petals and is an essential gene in plants.
Figures


References
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408: 796–815 - PubMed
-
- Bechtold N, Ellis J, Pelletier G (1993) In planta Agrobacterium mediated gene transfer by infiltration of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants. C R Acad Sci 316: 1194–1199 - PubMed
-
- Bowman JL, Smyth DR, Meyerowitz EM (1991) Genetic interactions among floral homeotic genes of Arabidopsis. Development 112: 1–20 - PubMed
-
- Brett D, Hanke J, Lehmann G, Haase S, Delbruck S, Krueger S, Reich J, Borka P (2000) EST comparison indicates 38% of human mRNAs contain possible alternative splice forms. FEBS Lett 474: 83–86 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

