Chimeric influenza A viruses with a functional influenza B virus neuraminidase or hemagglutinin
- PMID: 12915528
- PMCID: PMC187417
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.17.9116-9123.2003
Chimeric influenza A viruses with a functional influenza B virus neuraminidase or hemagglutinin
Abstract
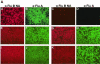
Reassortment of influenza A and B viruses has never been observed in vivo or in vitro. Using reverse genetics techniques, we generated recombinant influenza A/WSN/33 (WSN) viruses carrying the neuraminidase (NA) of influenza B virus. Chimeric viruses expressing the full-length influenza B/Yamagata/16/88 virus NA grew to titers similar to that of wild-type influenza WSN virus. Recombinant viruses in which the cytoplasmic tail or the cytoplasmic tail and the transmembrane domain of the type B NA were replaced with those of the type A NA were impaired in tissue culture. This finding correlates with reduced NA content in virions. We also generated a recombinant influenza A virus expressing a chimeric hemagglutinin (HA) protein in which the ectodomain is derived from type B/Yamagata/16/88 virus HA, whereas both the cytoplasmic and the transmembrane domains are derived from type A/WSN virus HA. This A/B chimeric HA virus did not grow efficiently in MDCK cells. However, after serial passage we obtained a virus population that grew to titers as high as wild-type influenza A virus in MDCK cells. One amino acid change in position 545 (H545Y) was found to be responsible for the enhanced growth characteristics of the passaged virus. Taken together, we show here that the absence of reassortment between influenza viruses belonging to different A and B types is not due to spike glycoprotein incompatibility at the level of the full-length NA or of the HA ectodomain.
Figures



References
-
- Baigent, S. J., and J. W. McCauley. 2001. Glycosylation of haemagglutinin and stalk-length of neuraminidase combine to regulate the growth of avian influenza viruses in tissue culture. Virus Res. 79:177-185. - PubMed
-
- Crescenzo-Chaigne, B., N. Naffakh, and S. van der Werf. 1999. Comparative analysis of the ability of the polymerase complexes of influenza viruses types A, B, and C to assemble into functional RNPs that allow expression and replication of heterotypic model RNA templates in vivo. Virology 265:342-353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

