Transforming growth factor beta1 receptor II is downregulated by E1A in adenovirus-infected cells
- PMID: 12915548
- PMCID: PMC187388
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.17.9324-9336.2003
Transforming growth factor beta1 receptor II is downregulated by E1A in adenovirus-infected cells
Abstract
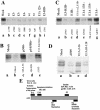
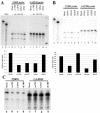
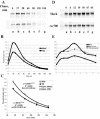
Transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) signaling is compromised in many tumors, thereby allowing the tumor to escape the growth-inhibitory and proapoptotic activities of the cytokine. Human adenoviruses interfere with a number of cellular pathways involved in cell cycle regulation and apoptosis, initially placing the cell in a "tumor-like" state by forcing quiescent cells into the cell cycle and also inhibiting apoptosis. We report that adenovirus-infected cells resemble tumor cells in that TGF-beta1 signaling is inhibited. The levels of TGF-beta1 receptor II (TbetaRII) in adenovirus-infected cells were decreased, and this decrease was mapped, by using virus mutants, to the E1A gene and to amino acids 2 to 36 and the C-terminal binding protein binding site in the E1A protein. The decrease in the TbetaRII protein was accompanied by a decrease in TbetaRII mRNA. The decrease in TbetaRII protein levels in adenovirus-infected cells was greater than the decrease in TbetaRII mRNA, suggesting that downregulation of the TbetaRII protein may occur through more than one mechanism. Surprisingly in this context, the half-lives of the TbetaRII protein in infected and uninfected cells were similar. TGF-beta1 signaling was compromised in cells infected with wild-type adenovirus, as measured with 3TP-lux, a TGF-beta-sensitive reporter plasmid expressing luciferase. Adenovirus mutants deficient in TbetaRII downregulation did not inhibit TGF-beta1 signaling. TGF-beta1 pretreatment reduced the relative abundance of adenovirus structural proteins in infected cells, an effect that was potentiated when cells were infected with mutants incapable of modulating the TGF-beta signaling pathway. These results raise the possibility that inhibition of TGF-beta signaling by E1A is a means by which adenovirus counters the antiviral defenses of the host.
Figures
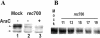
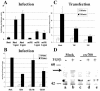
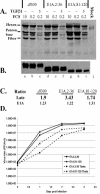
References
-
- Adnane, J., E. Seijo, Z. Chen, F. Bizouarn, M. Leal, S. M. Sebti, and T. Munoz-Antonia. 2002. RhoB, not RhoA represses the transcription of the transforming growth factor β type II receptor by a mechanism involving activator protein 1. J. Biol. Chem. 277:8500-8507. - PubMed
-
- Benedict, C., P. Norris, T. Prigozy, J. L. Bodmer, J. A. Mahr, C. Garnett, F. Martinon, J. Tschopp, L. R. Gooding, and C. F. Ware. 2001. Three adenovirus E3 proteins cooperate to evade apoptosis by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor-1 and -2. J. Biol. Chem. 276:3270-3278. - PubMed
-
- Bishopric, N. H., G.-Q. Zeng, B. Sato, and K. A. Webster. 1997. Adenovirus E1A inhibits cardiac myocyte-specific gene expression through its amino terminus. J. Biol. Chem. 272:20584-20594. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

