Comparative study of regulation of RTA-responsive genes in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8
- PMID: 12915560
- PMCID: PMC187374
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.17.9451-9462.2003
Comparative study of regulation of RTA-responsive genes in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8
Abstract
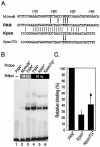
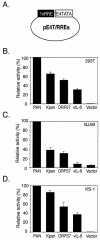
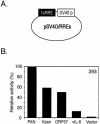
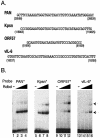
Replication and transcription activator (RTA) (also referred to as ORF50), an immediate-early gene product of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)/(human herpesvirus 8), plays a critical role in balancing the viral life cycle between latency and lytic replication. RTA has been shown to act as a strong transcription activator for several downstream genes of KSHV. Direct binding of RTA to DNA is thought to be one of the important mechanisms for transactivation of target genes, while indirect mechanisms are also implicated in RTA transactivation of certain selected genes. This study demonstrated direct binding of the DNA-binding domain of RTA (Rdbd) to a Kaposin (Kpsn) promoter sequence, which is highly homologous to the RTA-responsive element (RRE) of the PAN promoter. We undertook a comparative study of the RREs of PAN RNA, ORF57, vIL-6, and Kpsn to understand how RTA regulates gene expression during lytic replication. Comparing RNA abundance and transcription initiation rates of these RTA target genes in virus-infected cells suggested that the transcription initiation rate of the promoters is a major determinant of viral gene expression, rather than stability of the transcripts. RTA-mediated transactivation of reporters containing each RRE showed that their promoter strengths in a transient-transfection system were comparable to their transcription rates during reactivation. Moreover, our electrophoretic mobility shift assays of each RRE demonstrated that the highly purified Rdbd protein directly bound to the RREs. Based on these results, we conclude that direct binding of RTA to these target sequences contributes to their gene expression to various extents during the lytic life cycle of KSHV.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-alpha is induced during the early stages of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) lytic cycle reactivation and together with the KSHV replication and transcription activator (RTA) cooperatively stimulates the viral RTA, MTA, and PAN promoters.J Virol. 2003 Sep;77(17):9590-612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.17.9590-9612.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12915572 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of interactions between RTA and the promoter of polyadenylated nuclear RNA in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8.J Virol. 2002 May;76(10):5000-13. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.10.5000-5013.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11967316 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) in activation of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) lytic-cycle replication-associated protein (RAP) promoter in cooperation with the KSHV replication and transcription activator (RTA) and RAP.J Virol. 2003 Jan;77(1):600-23. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.1.600-623.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12477864 Free PMC article.
-
The Rta/Orf50 transactivator proteins of the gamma-herpesviridae.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007;312:71-100. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-34344-8_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17089794 Review.
-
Lytic cycle switches of oncogenic human gammaherpesviruses.Adv Cancer Res. 2007;97:81-109. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(06)97004-3. Adv Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17419942 Review.
Cited by
-
The RBP-Jκ binding sites within the RTA promoter regulate KSHV latent infection and cell proliferation.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Jan;8(1):e1002479. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002479. Epub 2012 Jan 12. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22253595 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8 ORF50/Rta lytic switch protein functions as a tetramer.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(11):5788-806. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00140-07. Epub 2007 Mar 28. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17392367 Free PMC article.
-
A Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8 ORF50 deletion mutant is defective for reactivation of latent virus and DNA replication.J Virol. 2005 Mar;79(6):3479-87. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.6.3479-3487.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15731242 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus Rta tetramers make high-affinity interactions with repetitive DNA elements in the Mta promoter to stimulate DNA binding of RBP-Jk/CSL.J Virol. 2011 Nov;85(22):11901-15. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05479-11. Epub 2011 Aug 31. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21880753 Free PMC article.
-
A mobile functional region of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF50 protein independently regulates DNA binding and protein abundance.J Virol. 2008 Oct;82(19):9700-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00862-08. Epub 2008 Jul 23. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18653447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cannon, J. S., J. Nicholas, J. M. Orenstein, R. B. Mann, P. G. Murray, P. J. Browning, J. A. DiGiuseppe, E. Cesarman, G. S. Hayward, and R. F. Ambinder. 1999. Heterogeneity of viral IL-6 expression in HHV-8-associated diseases. J. Infect. Dis. 180:824-828. - PubMed
-
- Cesarman, E., Y. Chang, P. S. Moore, J. W. Said, and D. M. Knowles. 1995. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 332:1186-1191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

