Pre-s1 antigen-dependent infection of Tupaia hepatocyte cultures with human hepatitis B virus
- PMID: 12915565
- PMCID: PMC187384
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.17.9511-9521.2003
Pre-s1 antigen-dependent infection of Tupaia hepatocyte cultures with human hepatitis B virus
Erratum in
- J Virol. 2005 Nov;79(22):14470
Abstract
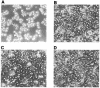
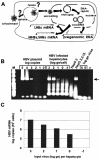
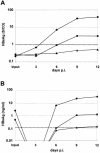
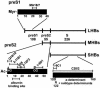
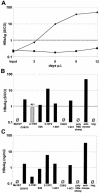
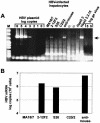
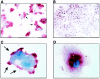
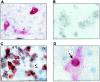
The susceptibility of the tree shrew Tupaia belangeri to human hepatitis B virus (HBV) has been demonstrated both in vivo and in vitro. In this study, we show that purified HBV infects primary T. belangeri hepatocyte cultures in a very specific manner, as detected by HBV covalently closed circular DNA, mRNA, HBV e antigen, and HBsAg production. A monoclonal antibody (MAb), MA18/7, directed against the pre-S1 domain of the large HBs protein, which has been shown to neutralize infectivity of HBV for primary human hepatocytes, also blocked infection of primary Tupaia hepatocytes. MAbs against the pre-S2 domain of HBs inhibited infection only partially, whereas an S MAb and polyvalent anti-HBs antibodies neutralized infection completely. Thus, both pre-S1 and S antigens are necessary for infection in the tupaia. Using subviral particles, >70% of primary Tupaia hepatocytes are capable of specific binding of pre-S1-rich HBsAg, showing localization in distinct membrane areas. The data show that the early steps of HBV infection in Tupaia hepatocyte cultures are comparable to those in the human system.
Figures
References
-
- Aldrich, C. E., L. Coates, T. T. Wu, J. Newbold, B. C. Tennant, J. Summers, C. Seeger, and W. S. Mason. 1989. In vitro infection of woodchuck hepatocytes with woodchuck hepatitis virus and ground squirrel hepatitis virus. Virology 172:247-252. - PubMed
-
- Cooreman, M. P., G. Leroux-Roels, and W. P. Paulij. 2001. Vaccine- and hepatitis B immune globulin-induced escape mutations of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. J. Biomed. Sci. 8:237-247. - PubMed
-
- Dandri, M., M. R. Burda, E. Torok, J. M. Pollok, A. Iwanska, G. Sommer, X. Rogiers, C. E. Rogler, S. Gupta, H. Will, H. Greten, and J. Petersen. 2001. Repopulation of mouse liver with human hepatocytes and in vivo infection with hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 33:981-988. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

