Randomized study of high-dose and low-dose interleukin-2 in patients with metastatic renal cancer
- PMID: 12915604
- PMCID: PMC2275327
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2003.02.122
Randomized study of high-dose and low-dose interleukin-2 in patients with metastatic renal cancer
Abstract
Purpose: This three-arm randomized study compares response rates and overall survival of patients with metastatic renal cell cancer (RCC) receiving high-dose or one of two low-dose interleukin-2 (IL-2) regimens.
Patients and methods: Patients with measurable metastatic RCC and a good performance status were randomized to receive either 720,000 U/kg (high-dose [HD]) or 72,000 U/kg (low-dose [LD]), both given by intravenous (IV) bolus every 8 hours. After randomly assigning 117 patients, a third arm of low-dose daily subcutaneous IL-2 was added, and an additional 283 patients were randomly assigned.
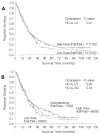
Results: A total of 156 patients were randomly assigned to HD IV IL-2, and 150 patients to LD IV IL-2. Toxicities were less frequent with LD IV IL-2 (especially hypotension), but there were no IL-2-related deaths in any arm. There was a higher response proportion with HD IV IL-2 (21%) versus LD IV IL-2 (13%; P =.048) but no overall survival difference. The response rate of subcutaneous IL-2 (10%, partial response and complete response) was similar to that of LD IV IL-2, differing from HD IV (P =.033). Response durability and survival in completely responding patients was superior with HD IV compared with LD IV therapy (P =.04).
Conclusion: Major tumor regressions, as well as complete responses, were seen with all regimens tested. IL-2 was more clinically active at maximal doses, although this did not produce an overall survival benefit. The immunological factors which constrain the curative potential of IL-2 to only a small percentage of patients need to be further elucidated.
Figures

References
-
- Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT, Muul L, et al. Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1985;313:1485–1492. - PubMed
-
- Lotze MT, Chang AE, Seipp CA, et al. High-dose recombinant interleukin 2 in the treatment of patients with disseminated cancer: Responses, treatment-related morbidity and histologic findings. JAMA. 1986;256:3117–3124. - PubMed
-
- Fisher RI, Rosenberg SA, Sznol M, et al. High-dose aldesleukin in renal cell carcinoma: Long-term survival update. Cancer J Sci Am. 1997;3(suppl 1):S70–S72. - PubMed
-
- Parkinson DR, Abrams JS, Wiernik PH, et al. Interleukin-2 therapy in patients with metastatic malignant melanoma: A phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 1990;8:1650–1656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

