Comparison of quality of life and arm complaints after axillary lymph node dissection vs sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer patients
- PMID: 12915872
- PMCID: PMC2376906
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601150
Comparison of quality of life and arm complaints after axillary lymph node dissection vs sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer patients
Abstract
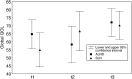
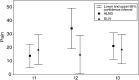
The sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) represents a minimal invasive surgical method for axillary staging in patients with primary breast cancer. In a prospective study, evaluation of quality of life (QOL) and arm morbidity was performed before surgery on a total of 56 breast cancer patients. The EORTC QLQ-C30 and EORTC QLQ-BR23 questionnaires were used for QOL assessment. Assessment of pain was additionally observed using the McGill Pain Questionnaire. Arm mobility was observed by goniometric measurement of arm movement. Data were collected before surgery (t1), 1 week after discharge (t2) and 9-12 months after surgery (t3). The type of axillary surgery does not seem to affect global QOL at a short-time follow-up, but patients recover sooner after SLNB. Body image and sexual functioning remain stable in both types of axillary surgery. Arm/shoulder pain was reported in 36% of patients after SLNB in comparison to 68% receiving axillary lymph node dissection (ALND), and 'numbness' was reported only in 4% of patients in the SLNB group vs 19.3% after ALND. Abduction, flexion and horizontal adduction of the affected arm show significant impairment after ALND. Breast cancer patients should be counselled about the benefits of SLNB over ALND concerning QOL and postsurgery side effects in a short-term follow-up.
Figures
References
-
- Aaronson NK, Ahmedzai S, Bergman B, Bullinger M, Cull A, Duez N, Filiberti A, Flechtner H, Fleishman SB, de Haes JC, Kaasa S, Klee M, Osoba D, Razavi D, Rofe PB, Schraub S, Sneeuw K, Sullivan M, Takeda F, for the European Organization for Research Treatment of Cancer Study Group on Quality of Life (1993) The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30: a quality-of-life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. J Natl Cancer Inst 85: 365–376 - PubMed
-
- Burak WE, Hollenbeck ST, Zervos EE, Hock KL, Kemp LC, Young DC (2002) Sentinel lymph node biopsy results in less postoperative morbidity compared with axillary lymph node dissection for breast cancer. Am J Surg 183: 23–27 - PubMed
-
- Carter CL, Allen C, Henson DE (1989) Relation of tumor size, lymph node status and survival in 24,740 breast cancer cases. Cancer 63: 181–187 - PubMed
-
- Coscarelli Schag CA, Ganz PA, Polinsky ML, Fred C, Hirji K, Petersen L (1993) Characteristics of women at risk for psychosocial distress in the year after breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 11: 783–793 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical