Three-dimensional rotational myelography
- PMID: 12917114
- PMCID: PMC7973654
Three-dimensional rotational myelography
Abstract
Three-dimensional (3D) rotational radiography, initially developed to visualize intracranial aneurysms, is applied to the cervical spine after conventional myelography. We call this process 3D rotational myelography. 3D reconstruction and then postprocessing allows imaging in multiple planes. Spinal or nerve root sheath alterations caused by bony or soft tissue can be visualized and differentiated by using this technique.
Figures
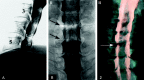

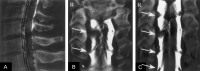

References
-
- Voigt K, Stoeter P, Petersen D. Rotational cerebral roentgenography: I. evaluation of the technical procedure and diagnostic application with model studies. Neuroradiology 1975;10:95–100 - PubMed
-
- Wiesent K, Barth K, Navab N, et al. Enhanced 3-D-reconstruction algorithm for C-arm systems suitable for interventional procedures. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2000;19:391–403 - PubMed
-
- Daniels DL, Grogan JP, Johansen JG, Meyer GA, Williams AL, Haughton VM. Cervical radiculopathy: computed tomography and myelography compared. Radiology 1984;151:109–113 - PubMed
-
- Larsson EM, Holtas S, Cronqvist S, Brandt L. Comparison of myelography, CT myelography and magnetic resonance imaging in cervical spondylosis and disk herniation: pre- and postoperative findings. Acta Radiol 1989;30:233–239 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
