Non-contrast-enhanced CT findings of high attenuation within metastatic cervical lymph nodes in patients with stage I or II tongue carcinoma during a follow-up period
- PMID: 12917122
- PMCID: PMC7973692
Non-contrast-enhanced CT findings of high attenuation within metastatic cervical lymph nodes in patients with stage I or II tongue carcinoma during a follow-up period
Abstract
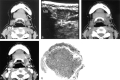
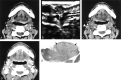
We present the non-contrast-enhanced CT finding of high attenuation within metastatic regional lymph nodes in two patients with stage I or II tongue carcinoma during a follow-up period. The attenuation values of these lesions were approximately 70 HU or more. One patient had a level I node, and the other had a level II node. Contrast-enhanced CT failed to reveal these hyperattenuated areas within the nodes. Histopathologic examination revealed that these hyperattenuated areas were strongly correlated with the area of marked keratinization of metastatic foci. If contrast-enhanced CT had been the only imaging technique used, these lesions might have been overlooked. The clinician should be aware of the characteristic findings of non-contrast-enhanced, as well as contrast-enhanced, CT when investigating lymph node metastases at an early stage in patients with stage I or II tongue carcinoma during the follow-up period.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The clinical significance of follow-up sonography in the detection of cervical lymph node metastases in patients with stage I or II squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2003 Jul;96(1):112-7. doi: 10.1016/s1079-2104(03)00259-2. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2003. PMID: 12847453
-
Preliminary study of indirect CT lymphography-guided sentinel lymph node biopsy in a tongue VX2 carcinoma model.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009 Dec;38(12):1268-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2009.07.009. Epub 2009 Aug 12. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009. PMID: 19679448
-
Assessment of cervical lymph node metastases using indirect computed tomography lymphography with iopamidol in a tongue VX2 carcinoma model.J Laryngol Otol. 2011 Aug;125(8):820-8. doi: 10.1017/S0022215111000958. Epub 2011 May 31. J Laryngol Otol. 2011. PMID: 21729450
-
The role of ultrasound in primary workup of cervical cancer staging (ESGO, ESTRO, ESP cervical cancer guidelines).Ceska Gynekol. 2019 Winter;84(1):40-48. Ceska Gynekol. 2019. PMID: 31213057 Review. English.
-
Sentinel lymphatic mapping among women with early-stage cervical cancer: A systematic review.Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Oct;57(5):636-643. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2018.08.004. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 30342642
Cited by
-
CD147 and Ki-67 overexpression confers poor prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma of oral tongue: a tissue microarray study.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2015 May;119(5):553-65. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2014.12.022. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25747176 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of magnetic resonance imaging accuracy for diagnosis of oral cancer.PLoS One. 2017 May 24;12(5):e0177462. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177462. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28542622 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prince S, Bailey BM. Squamous carcinoma of the tongue: review. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1999;37:164–174 - PubMed
-
- Haddadin KJ, Soutar DS, Oliver RJ, et al. Improved survival for patients with clinically T1/T2, N0 tongue tumors undergoing a prophylactic neck dissection. Head Neck 1999;21:517–525 - PubMed
-
- Beenken SW, Krontiras H, Maddox WA, et al. T1 and T2 squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue: prognostic factors and the role of elective lymph node dissection. Head Neck 1999;21:124–130 - PubMed
-
- Yuen AP, Lam KY, Chan AC, et al. Clinicopathological analysis of elective neck dissection for N0 neck of early oral tongue carcinoma. Am J Surg 1999;177:90–92 - PubMed
-
- Yii NW, Patel SG, Rhys-Evans PH, Breach NM. Management of the N0 neck in early cancer of the oral tongue. Clin Otolaryngol 1999;24:75–79 - PubMed
