Massive epistaxis related to petrous carotid artery pseudoaneurysm after radiation therapy: emergency treatment with covered stent in two cases
- PMID: 12917144
- PMCID: PMC7973657
Massive epistaxis related to petrous carotid artery pseudoaneurysm after radiation therapy: emergency treatment with covered stent in two cases
Abstract
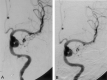
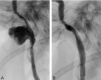
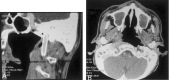
Two patients had acute left carotid rupture from radiation therapy-induced pseudoaneurysms, resulting in hemodynamic collapse. Because the patients were semicomatose and in shock, an immediate salvage procedure was needed. Location of the pseudoaneurysm at the skull base made surgical treatment less possible. Endovascular therapy was the treatment of choice. Preserving patency of the carotid artery was a desirable option. The successful use of a covered stent in the emergency treatment of massive epistaxis due to active bleeding from pseudoaneurysm in the petrous internal carotid artery (ICA) is described.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The use of a covered stent graft for obliteration of high-flow carotid cavernous fistula presenting with life-threatening epistaxis.J Neurointerv Surg. 2009 Dec;1(2):142-5. doi: 10.1136/jnis.2009.001040. Epub 2009 Oct 30. J Neurointerv Surg. 2009. PMID: 21994284
-
Treatment of an iatrogenic petrous carotid artery pseudoaneurysm with a Symbiot covered stent: technical case report.Neurosurgery. 2002 Mar;50(3):658-62. doi: 10.1097/00006123-200203000-00047. Neurosurgery. 2002. PMID: 11841739
-
Intractable epistaxis related to cavernous carotid artery pseudoaneurysm: treatment of a case with covered stent.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2004 Sep;31(3):275-8. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2004.03.007. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2004. PMID: 15364363
-
Retrospective analysis of massive epistaxis and pseudoaneurysms in nasopharyngeal carcinoma after radiotherapy.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Jun;279(6):2973-2980. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-07111-x. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 34623497 Review.
-
Rupture from cavernous internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm 11 years after transsphenoidal surgery.J Clin Neurosci. 2020 Sep;79:266-268. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2020.06.018. Epub 2020 Aug 25. J Clin Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33070909 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical findings and imaging features of 67 nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients with postradiation nasopharyngeal necrosis.Chin J Cancer. 2013 Oct;32(10):533-8. doi: 10.5732/cjc.012.10252. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Chin J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23816556 Free PMC article.
-
Meningitis and brain abscess presenting with epistaxis in a woman with prior head and neck cancer.Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2015;2015:460208. doi: 10.1155/2015/460208. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2015. PMID: 25883822 Free PMC article.
-
Covered stent graft for treatment of a pseudoaneurysm and carotid blowout syndrome.J Vasc Interv Neurol. 2008 Jan;1(1):5-8. J Vasc Interv Neurol. 2008. PMID: 22518207 Free PMC article.
-
Angiographic follow-up of traumatic carotid cavernous fistulas treated with endovascular stent graft placement.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007 Feb;28(2):342-7. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007. PMID: 17297009 Free PMC article.
-
Endovascular treatment of a temporal bone pseudoaneurysm presenting as bloody otorrhea.J Neurol Surg Rep. 2013 Dec;74(2):88-91. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1348954. Epub 2013 Jul 12. J Neurol Surg Rep. 2013. PMID: 24294565 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batjer HH, Mickey B, Samson DS. Enlargement and rupture of distal basilar artery aneurysm after iatrogenic carotid occlusion. Neurosurgery 1987;20:624–628 - PubMed
-
- Yamanaka C, Hirohata T, Kiya K, Yoshimoto H, Uozumi T. Basilar bifurcation aneurysm associated with bilateral internal carotid occlusion. Neuroradiology 1987;29:84–88 - PubMed
-
- Larson JJ, Tew JM Jr, Tomsick TA, van Loveren HR. Treatment of aneurysms of the internal carotid artery by intravascular balloon occlusion: long-term follow-up of 58 patients. Neurosurgery 1995;36:26–30 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
