Massive epistaxis related to petrous carotid artery pseudoaneurysm after radiation therapy: emergency treatment with covered stent in two cases
- PMID: 12917144
- PMCID: PMC7973657
Massive epistaxis related to petrous carotid artery pseudoaneurysm after radiation therapy: emergency treatment with covered stent in two cases
Abstract
Two patients had acute left carotid rupture from radiation therapy-induced pseudoaneurysms, resulting in hemodynamic collapse. Because the patients were semicomatose and in shock, an immediate salvage procedure was needed. Location of the pseudoaneurysm at the skull base made surgical treatment less possible. Endovascular therapy was the treatment of choice. Preserving patency of the carotid artery was a desirable option. The successful use of a covered stent in the emergency treatment of massive epistaxis due to active bleeding from pseudoaneurysm in the petrous internal carotid artery (ICA) is described.
Figures
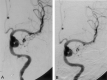
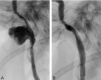
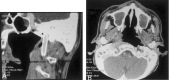
References
-
- Batjer HH, Mickey B, Samson DS. Enlargement and rupture of distal basilar artery aneurysm after iatrogenic carotid occlusion. Neurosurgery 1987;20:624–628 - PubMed
-
- Yamanaka C, Hirohata T, Kiya K, Yoshimoto H, Uozumi T. Basilar bifurcation aneurysm associated with bilateral internal carotid occlusion. Neuroradiology 1987;29:84–88 - PubMed
-
- Larson JJ, Tew JM Jr, Tomsick TA, van Loveren HR. Treatment of aneurysms of the internal carotid artery by intravascular balloon occlusion: long-term follow-up of 58 patients. Neurosurgery 1995;36:26–30 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
