Yaf9, a novel NuA4 histone acetyltransferase subunit, is required for the cellular response to spindle stress in yeast
- PMID: 12917332
- PMCID: PMC180919
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.17.6086-6102.2003
Yaf9, a novel NuA4 histone acetyltransferase subunit, is required for the cellular response to spindle stress in yeast
Abstract
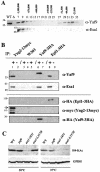
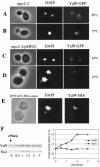
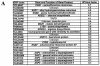
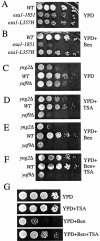
Yaf9 is one of three proteins in budding yeast containing a YEATS domain. We show that Yaf9 is part of a large complex and that it coprecipitates with three known subunits of the NuA4 histone acetyltransferase. Although Esa1, the catalytic subunit of NuA4, is essential for viability, we found that yaf9 Delta mutants are viable but hypersensitive to microtubule depolymerizing agents and synthetically lethal with two different mutants of the mitotic apparatus. Microtubules depolymerized more readily in the yaf9Delta mutant compared to the wild type in the presence of nocodazole, and recovery of microtubule polymerization and cell division from limiting concentrations of nocodazole was inhibited. Two other NuA4 mutants (esa1-1851 and yng2 Delta) and nonacetylatable histone H4 mutants were also sensitive to benomyl. Furthermore, wild-type budding yeast were more resistant to benomyl when grown in the presence of trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor. These results strongly suggest that acetylation of histone H4 by NuA4 is required for the cellular resistance to spindle stress.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Yaf9 component of the SWR1 and NuA4 complexes is required for proper gene expression, histone H4 acetylation, and Htz1 replacement near telomeres.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Nov;24(21):9424-36. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.21.9424-9436.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15485911 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple links between the NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex and epigenetic control of transcription.Mol Cell. 2000 Jun;5(6):927-37. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80258-0. Mol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10911987
-
NuA4 subunit Yng2 function in intra-S-phase DNA damage response.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Dec;22(23):8215-25. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.23.8215-8225.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12417725 Free PMC article.
-
Reading chromatin: insights from yeast into YEATS domain structure and function.Epigenetics. 2010 Oct 1;5(7):573-7. doi: 10.4161/epi.5.7.12856. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Epigenetics. 2010. PMID: 20657183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone acetylation and deacetylation in yeast.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Apr;4(4):276-84. doi: 10.1038/nrm1075. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12671650 Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive synthetic genetic interaction network governing yeast histone acetylation and deacetylation.Genes Dev. 2008 Aug 1;22(15):2062-74. doi: 10.1101/gad.1679508. Genes Dev. 2008. PMID: 18676811 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of chromosome stability by the histone H2A variant Htz1, the Swr1 chromatin remodeling complex, and the histone acetyltransferase NuA4.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Sep 14;101(37):13513-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405753101. Epub 2004 Sep 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15353583 Free PMC article.
-
The YEATS domain of Taf14 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae has a negative impact on cell growth.Mol Genet Genomics. 2010 Apr;283(4):365-80. doi: 10.1007/s00438-010-0523-x. Epub 2010 Feb 24. Mol Genet Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20179968 Free PMC article.
-
Structure/function analysis of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase domain of yeast tra1.Genetics. 2007 Sep;177(1):151-66. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.074476. Epub 2007 Jul 29. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17660562 Free PMC article.
-
ENL: structure, function, and roles in hematopoiesis and acute myeloid leukemia.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 Nov;75(21):3931-3941. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2895-8. Epub 2018 Jul 31. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 30066088 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bilbao-Cortes, D., M. Hetzer, G. Langst, P. B. Becker, and I. W. Mattaj. 2002. Ran binds to chromatin by two distinct mechanisms. Curr. Biol. 12:1151-1156. - PubMed
-
- Bird, A. W., D. Y. Yu, M. G. Pray-Grant, Q. Qiu, K. E. Harmon, P. C. Megee, P. A. Grant, M. M. Smith, and M. F. Christman. 2002. Acetylation of histone H4 by Esa1 is required for DNA double-strand break repair. Nature 419:411-415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
