Potentiation of tumor necrosis factor-induced NF-kappa B activation by deacetylase inhibitors is associated with a delayed cytoplasmic reappearance of I kappa B alpha
- PMID: 12917341
- PMCID: PMC180966
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.17.6200-6209.2003
Potentiation of tumor necrosis factor-induced NF-kappa B activation by deacetylase inhibitors is associated with a delayed cytoplasmic reappearance of I kappa B alpha
Erratum in
- Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Aug;24(15):6890
Abstract
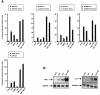
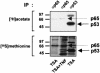
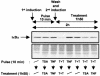
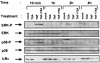
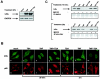
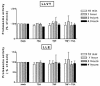
Previous studies have implicated acetylases and deacetylases in regulating the transcriptional activity of NF-kappa B. Here, we show that inhibitors of deacetylases such as trichostatin A (TSA) and sodium butyrate (NaBut) potentiated TNF-induced expression of several natural NF-kappa B-driven promoters. This transcriptional synergism observed between TNF and TSA (or NaBut) required intact kappa B sites in all promoters tested and was biologically relevant as demonstrated by RNase protection on two instances of endogenous NF-kappa B-regulated gene transcription. Importantly, TSA prolonged both TNF-induced DNA-binding activity and the presence of NF-kappa B in the nucleus. We showed that the p65 subunit of NF-kappa B was acetylated in vivo. However, this acetylation was weak, suggesting that other mechanisms could be implicated in the potentiated binding and transactivation activities of NF-kappa B after TNF plus TSA versus TNF treatment. Western blot and immunofluorescence confocal microscopy experiments revealed a delay in the cytoplasmic reappearance of the I kappa B alpha inhibitor that correlated temporally with the prolonged intranuclear binding and presence of NF-kappa B. This delay was due neither to a defect in I kappa B alpha mRNA production nor to a nuclear retention of I kappa B alpha but was rather due to a persistent proteasome-mediated degradation of I kappa B alpha. A prolongation of I kappa B kinase activity could explain, at least partially, the delayed I kappa B alpha cytoplasmic reappearance observed in presence of TNF plus TSA.
Figures



References
-
- Aoudjit, F., N. Brochu, B. Belanger, C. Stratowa, J. Hiscott, and M. Audette. 1997. Heterodimeric retinoic acid receptor-β and retinoid X receptor-α complexes stimulate expression of the intercellular adhesion molecule-1 gene. Cell Growth Differ. 8:335-342. - PubMed
-
- Arenzana-Seisdedos, F., P. Turpin, M. Rodriguez, D. Thomas, R. T. Hay, J. L. Virelizier, and C. Dargemont. 1997. Nuclear localization of IκBα promotes active transport of NF-κB from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. J. Cell Sci. 110:369-378. - PubMed
-
- Ben Neriah, Y. 2002. Regulatory functions of ubiquitination in the immune system. Nat. Immunol. 3:20-26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
