BAF60a mediates critical interactions between nuclear receptors and the BRG1 chromatin-remodeling complex for transactivation
- PMID: 12917342
- PMCID: PMC180928
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.17.6210-6220.2003
BAF60a mediates critical interactions between nuclear receptors and the BRG1 chromatin-remodeling complex for transactivation
Abstract
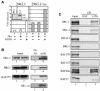
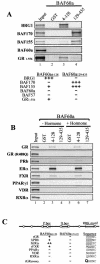
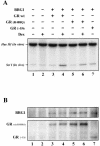
Nuclear hormone receptors are ligand-dependent transcriptional regulators that modulate chromatin structure. However, the precise molecular mechanisms by which receptors recruit chromatin-remodeling activity are not fully elucidated. We show that in the absence of its ligand-binding domain, the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is able to interact with both nuclear receptor coactivators and the BRG1 chromatin-remodeling complex in vivo. Individually, the GR makes direct interactions with BRG1-associated factor 60a (BAF60a) and BAF57, but not with BRG1, BAF155, or BAF170. Further, BAF60a possesses at least two interaction surfaces, one for GR and BRG1 and a second for BAF155 and BAF170. A GR mutant, GR(R488Q), that fails to interact with BAF60a in vitro has reduced chromatin-remodeling activity and reduced transcriptional activity from the promoter assembled as chromatin in vivo. Stable expression of a BAF60a truncation mutant, BAF60a4-140, caused chromatin-specific loss of GR functions in vivo. In the presence of the BAF60a mutant, the GR fails to interact with the BRG1 complex and consequently is also deficient in its ability to activate transcription from chromatin. Thus, in addition to previously identified BAF250, BAF60a may provide another critical and direct link between nuclear receptors and the BRG1 complex that is required for promoter recruitment and subsequent chromatin remodeling.
Figures




References
-
- Archer, T. K., P. Lefebvre, R. G. Wolford, and G. L. Hager. 1992. Transcription factor loading on the MMTV promoter: a bimodal mechanism for promoter activation. Science 255:1573-1576. - PubMed
-
- Archer, T. K., E. Zaniewski, M. L. Moyer, and S. K. Nordeen. 1994. The differential capacity of glucocorticoids and progestins to alter chromatin structure and induce gene expression in human breast cancer cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 8:1154-1162. - PubMed
-
- Becker, P. B., and W. Horz. 2002. ATP-dependent nucleosome remodeling. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71:247-273. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
