Phosphorylation of FREQUENCY protein by casein kinase II is necessary for the function of the Neurospora circadian clock
- PMID: 12917343
- PMCID: PMC180927
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.17.6221-6228.2003
Phosphorylation of FREQUENCY protein by casein kinase II is necessary for the function of the Neurospora circadian clock
Abstract
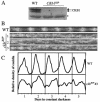
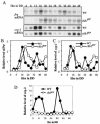
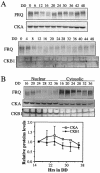
FREQUENCY (FRQ), a key component of the Neurospora circadian clock, is progressively phosphorylated after its synthesis. Previously, we identified casein kinase II (CKII) as a kinase that phosphorylates FRQ. Disruption of the catalytic subunit of CKII abolishes the clock function; it also causes severe defects in growth and development. To further establish the role of CKII in clock function, one of the CKII regulatory subunit genes, ckb1, was disrupted in Neurospora. In the ckb1 mutant strain, FRQ proteins are hypophosphorylated and more stable than in the wild-type strain, and circadian rhythms of conidiation and FRQ protein oscillation were observed to have long periods but low amplitudes. These data suggest that phosphorylation of FRQ by CKII regulates FRQ stability and the function of the circadian feedback loop. In addition, mutations of several putative CKII phosphorylation sites of FRQ led to hypophosphorylation of FRQ and long-period rhythms. Both CKA and CKB1 proteins are found in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus, but their expressions and localization are not controlled by the clock. Finally, disruption of a Neurospora casein kinase I (CKI) gene, ck-1b, showed that it is not required for clock function despite its important role in growth and developmental processes. Together, these data indicate that CKII is an important component of the Neurospora circadian clock.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Regulation of the Neurospora circadian clock by casein kinase II.Genes Dev. 2002 Apr 15;16(8):994-1006. doi: 10.1101/gad.965102. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 11959847 Free PMC article.
-
CKI and CKII mediate the FREQUENCY-dependent phosphorylation of the WHITE COLLAR complex to close the Neurospora circadian negative feedback loop.Genes Dev. 2006 Sep 15;20(18):2552-65. doi: 10.1101/gad.1463506. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16980584 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of posttranslational regulations in the Neurospora circadian clock.Methods Enzymol. 2005;393:379-93. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)93017-6. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 15817300
-
Posttranslational regulation of Neurospora circadian clock by CK1a-dependent phosphorylation.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007;72:177-83. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2007.72.025. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007. PMID: 18419275 Review.
-
A circadian clock in Neurospora: how genes and proteins cooperate to produce a sustained, entrainable, and compensated biological oscillator with a period of about a day.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007;72:57-68. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2007.72.072. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007. PMID: 18522516 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Posttranslational regulation of the mammalian circadian clock by cryptochrome and protein phosphatase 5.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jul 5;103(27):10467-10472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604138103. Epub 2006 Jun 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16790549 Free PMC article.
-
FWD1-mediated degradation of FREQUENCY in Neurospora establishes a conserved mechanism for circadian clock regulation.EMBO J. 2003 Sep 1;22(17):4421-30. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg425. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12941694 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the circadian clock system in physiology.Pflugers Arch. 2018 Feb;470(2):227-239. doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-2103-y. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 29302752 Review.
-
The Stress of Fungicides Changes the Expression of Clock Protein CmFRQ and the Morphology of Fruiting Bodies of Cordyceps militaris.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Feb 13;10(2):150. doi: 10.3390/jof10020150. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392822 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian rhythms in Neurospora crassa and other filamentous fungi.Eukaryot Cell. 2006 Aug;5(8):1184-93. doi: 10.1128/EC.00133-06. Eukaryot Cell. 2006. PMID: 16896204 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Akten, B., E. Jauch, G. K. Genova, E. Y. Kim, I. Edery, T. Raabe, and F. R. Jackson. 2003. A role for CK2 in the Drosophila circadian oscillator. Nat. Neurosci. 6:251-257. - PubMed
-
- Aronson, B., K. Johnson, J. J. Loros, and J. C. Dunlap. 1994. Negative feedback defining a circadian clock: autoregulation in the clock gene frequency. Science 263:1578-1584. - PubMed
-
- Bell-Pedersen, D., J. C. Dunlap, and J. J. Loros. 1992. The Neurospora circadian clock-controlled gene, ccg-2, is allelic to eas and encodes a fungal hydrophobin required for formation of the conidial rodlet layer. Genes Dev. 6:2382-2394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
