The role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway in mood modulation
- PMID: 12917364
- PMCID: PMC6740453
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-19-07311.2003
The role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway in mood modulation
Abstract
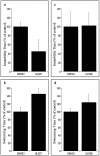
The neurobiological underpinnings of mood modulation, molecular pathophysiology of manic-depressive illness, and therapeutic mechanism of mood stabilizers are largely unknown. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway is activated by neurotrophins and other neuroactive chemicals to produce their effects on neuronal differentiation, survival, regeneration, and structural and functional plasticity. We found that lithium and valproate, commonly used mood stabilizers for the treatment of manic-depressive illness, stimulated the ERK pathway in the rat hippocampus and frontal cortex. Both drugs increased the levels of activated phospho-ERK44/42, activated phospho-ribosomal protein S6 kinase-1 (RSK1) (a substrate of ERK), phospho-CREB (cAMP response element-binding protein) and phospho-B cell lymphoma protein-2 antagonist of cell death (substrates of RSK), and BDNF. Inhibiting the ERK pathway with the blood-brain barrier-penetrating mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase)/ERK kinase (MEK) kinase inhibitor SL327, but not with the nonblood-brain barrier-penetrating MEK inhibitor U0126, decreased immobility time and increased swimming time of rats in the forced-swim test. SL327, but not U0126, also increased locomotion time and distance traveled in a large open field. The behavioral changes in the open field were prevented with chronic lithium pretreatment. SL327-induced behavioral changes are qualitatively similar to the changes induced by amphetamine, a compound that induces relapse in remitted manic patients and mood elevation in normal subjects. These data suggest that the ERK pathway may mediate the antimanic effects of mood stabilizers.
Figures



References
-
- Chuang DM, Chen R, Chalecka-Franaszek E, Ren M, Hashimoto R, Senatorov V, Kanai H, Hough C, Hiroi T, Leeds P ( 2002) Neuroprotective effects of lithium in cultured cells and animal model of diseases. Bipolar Disord 4: 129-136. - PubMed
-
- Coyle JT, Duman RS ( 2003) Finding the intracellular signaling pathways affected by mood disorder treatments. Neuron 38: 157-160. - PubMed
-
- Dawson TM, Ginty DD ( 2002) CREB family transcription factors inhibit neuronal suicide. Nat Med 8: 450-451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
