GCP II (NAALADase) inhibition suppresses mossy fiber-CA3 synaptic neurotransmission by a presynaptic mechanism
- PMID: 12917384
- PMCID: PMC2810521
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00465.2003
GCP II (NAALADase) inhibition suppresses mossy fiber-CA3 synaptic neurotransmission by a presynaptic mechanism
Abstract
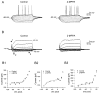
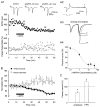
We tested the hypothesis that endogenous N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG) presynaptically inhibits glutamate release at mossy fiber-CA3 synapses. For this purpose, we made use of 2-(3-mercaptopropyl)pentanedioic acid (2-MPPA), an inhibitor of glutamate carboxypeptidase II [GCP II; also known as N-acetylated alpha-linked acidic dipeptidase (NAALADase)], the enzyme that hydrolyzes NAAG into N-acetylaspartate and glutamate. Application of 2-MPPA (1-20 microM) had no effect on intrinsic membrane properties of CA3 pyramidal neurons recorded in vitro in whole cell current- or voltage-clamp mode. Bath application of 10 microM 2-MPPA suppressed evoked excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC) amplitudes. Attenuation of EPSC amplitudes was accompanied by a significant increase in paired-pulse facilitation (50-ms interpulse intervals), suggesting that a presynaptic mechanism is involved. The group II metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR) antagonist 2S-2-amino-2-(1S,2S-2-carboxycyclopropyl-1-yl)-3-(xanth-9-y l) propanoic acid (LY341495) prevented the 2-MPPA-dependent suppression of EPSC amplitudes. 2-MPPA reduced the frequencies of TTX-insensitive miniature EPSCs (mEPSC), without affecting their amplitudes, further supporting a presynaptic action for GCP II inhibition. 2-MPPA-induced reduction of mEPSC frequencies was prevented by LY341495, reinforcing the role of presynaptic group II mGluR. Because GCP II inhibition is thought to increase NAAG levels, these results suggest that NAAG suppresses synaptic transmission at mossy fiber-CA3 synapses through presynaptic activation of group II mGluRs.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission by endogenous glutamate acting on presynaptic group II mGluRs in rat substantia nigra compacta.J Neurosci Res. 2005 Dec 15;82(6):778-87. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20694. J Neurosci Res. 2005. PMID: 16273546
-
Presynaptic inhibition of corticothalamic feedback by metabotropic glutamate receptors.J Neurophysiol. 2005 Jul;94(1):163-75. doi: 10.1152/jn.01198.2004. Epub 2005 Mar 16. J Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 15772234
-
Activation of presynaptic P2X7-like receptors depresses mossy fiber-CA3 synaptic transmission through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase.J Neurosci. 2002 Jul 15;22(14):5938-45. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-14-05938.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12122056 Free PMC article.
-
Role of giant depolarizing potentials in shaping synaptic currents in the developing hippocampus.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006;18(1-2):13-23. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v18.i1-2.30. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 17725505 Review.
-
How addictive drugs disrupt presynaptic dopamine neurotransmission.Neuron. 2011 Feb 24;69(4):628-49. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.02.010. Neuron. 2011. PMID: 21338876 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
2-MPPA, a selective glutamate carboxypeptidase II inhibitor, attenuates morphine tolerance but not dependence in C57/Bl mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Dec;183(3):275-84. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-0182-5. Epub 2005 Oct 12. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 16220328
-
The Brain Metabolic Signature in Superagers Using In Vivo 1H-MRS: A Pilot Study.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021 Oct;42(10):1790-1797. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7262. Epub 2021 Aug 26. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021. PMID: 34446458 Free PMC article.
-
A role for the locus coeruleus in the analgesic efficacy of N-acetylaspartylglutamate peptidase (GCPII) inhibitors ZJ43 and 2-PMPA.Mol Pain. 2017 Jan;13:1744806917697008. doi: 10.1177/1744806917697008. Mol Pain. 2017. PMID: 28326936 Free PMC article.
-
Differential changes in mGlu2 and mGlu3 gene expression following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus: a comparative real-time PCR analysis.Brain Res. 2008 Aug 21;1226:173-80. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.05.073. Epub 2008 Jun 7. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18585369 Free PMC article.
-
Group II metabotropic glutamate receptors inhibit glutamate release at thalamocortical synapses in the developing somatosensory cortex.Neuroscience. 2007 May 25;146(3):1062-72. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.02.053. Epub 2007 Apr 6. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17418955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson KJ, Monaghan DT, Cangro CB, Namboodiri MA, Neale JH, Cotman CW. Localization of N-acetylaspartylglutamate-like immunoreactivity in selected areas of the rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1986;72:14–20. - PubMed
-
- Bacich DJ, Ramadan E, O’Keefe DS, Bukhari N, Wegorzewska I, Ojeifo O, Olszewski R, Wrenn CC, Bzdega T, Wroblewska B, Heston WD, Neale JH. Deletion of the glutamate carboxypeptidase II gene in mice reveals a second enzyme activity that hydrolyzes N-acetylaspartylglutamate. J Neurochem. 2002;83:20–29. - PubMed
-
- Bains JS, Longacher JM, Staley KJ. Reciprocal interactions between CA3 network activity and strength of recurrent collateral synapses. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:720–726. - PubMed
-
- Blumcke I, Behle K, Malitschek B, Kuhn R, Knopfel T, Wolf HK, Wiestler OD. Immunohistochemical distribution of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes mGluR1b, mGluR2/3, mGluR4a, and mGluR5 in human hippocampus. Brain Res. 1996;736:217–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

