B7x: a widely expressed B7 family member that inhibits T cell activation
- PMID: 12920180
- PMCID: PMC193571
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1434299100
B7x: a widely expressed B7 family member that inhibits T cell activation
Abstract
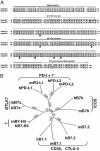
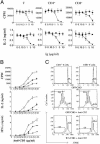
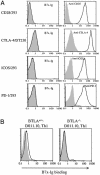
B7 family proteins provide costimulatory signals that regulate T cell responses. Here we report the third set of B7 family-related T cell inhibitory molecules with the identification of a homolog of the B7 family, B7x. It is expressed in immune cells, nonlymphoid tissues, and some tumor cell lines. B7x inhibits cell-cycle progression, proliferation, and cytokine production of both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. B7x binds a receptor that is expressed on activated, but not resting T cells that is distinct from known CD28 family members. Its receptor may be a recently identified inhibitory molecule, B and T lymphocyte attenuator. These studies identify a costimulatory pathway that may have a unique function in downregulation of tissue-specific autoimmunity and antitumor responses.
Figures

References
-
- Egen, J. G., Kuhns, M. S. & Allison, J. P. (2002) Nat. Immunol. 3, 611-618. - PubMed
-
- Sharpe, A. H. & Freeman, G. J. (2002) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 116-126. - PubMed
-
- Abbas, A. K. & Sharpe, A. H. (1999) Nat. Med. 5, 1345-1346. - PubMed
-
- Coyle, A. J. & Gutierrez-Ramos, J. C. (2001) Nat. Immunol. 2, 203-209. - PubMed
-
- Carreno, B. M. & Collins, M. (2002) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 29-53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

