Group interest versus self-interest in smallpox vaccination policy
- PMID: 12920181
- PMCID: PMC193525
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1731324100
Group interest versus self-interest in smallpox vaccination policy
Abstract
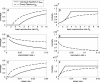
The recent threat of bioterrorism has fueled debate on smallpox vaccination policy for the United States. Certain policy proposals call for voluntary mass vaccination; however, if individuals decide whether to vaccinate according to self-interest, the level of herd immunity achieved may differ from what is best for the population as a whole. We present a synthesis of game theory and epidemic modeling that formalizes this conflict between self-interest and group interest and shows that voluntary vaccination is unlikely to reach the group-optimal level. This shortfall results in a substantial increase in expected mortality after an attack.
Figures
References
-
- Halloran, M. E., Longini, I. M., Nizam, A. & Yang, Y. (2002) Science 298, 1428-1432. - PubMed
-
- Cohen, J. & Enserink, M. (2002) Science 298, 2312-2316. - PubMed
-
- von Neumann, J. & Morgenstern, O. (1944) Theory of Games and Economic Behavior (Princeton Univ. Press, Princeton).
-
- Maynard-Smith, J. (1982) Evolution and the Theory of Games (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, U.K.).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

