Agonists for neuropeptide Y receptors Y1 and Y5 stimulate different phases of feeding in guinea pigs
- PMID: 12922930
- PMCID: PMC1573983
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705389
Agonists for neuropeptide Y receptors Y1 and Y5 stimulate different phases of feeding in guinea pigs
Abstract
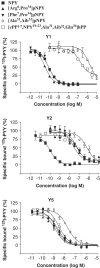
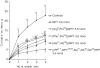
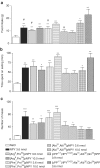
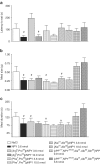
1. The stimulatory effect of neuropeptide Y (NPY) on food intake is well established but the roles of the receptor subtypes Y(1) and Y(5) have been difficult to define. We have studied the effects of two novel Y(1)-preferring and two Y(5)-preferring agonists on feeding in guinea pigs. 2. The Y(1)-preferring receptor agonists [Arg(6),Pro(34)]pNPY and [Phe(7),Pro(34)]pNPY had high affinity for the Y(1) receptor (K(i) values 0.07 and 0.04 nM, respectively) and nanomolar affinity for the Y(5) receptor. Administration of either compound into the third brain ventricle increased food intake equally to NPY. 3. The Y(5) agonist [Ala(31),Aib(32)]pNPY displayed a moderate affinity for the Y(5) receptor (K(i) 7.42 nM) and a low affinity for Y(1) (K(i) 1.7 micro M). This compound had only a modest effect on feeding. 4. The other Y(5)-preferring peptide [cPP(1-7),NPY(19-23),Ala(31),Aib(32),Gln(34)]hPP had a higher affinity at the Y(5) receptor (K(i) 1.32 nM) and also at the Y(1) receptor (K(i) 85 nM). It potently stimulated feeding: the food consumption after administration of this peptide was two-fold compared to NPY. 5. Our results support the view that both the receptor subtypes Y(1) and Y(5) are involved in the stimulation of feeding. As the action profiles of the Y(1) and Y(5) agonists on feeding parameters were different, it seems that they influence different phases of eating.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Receptor subtypes Y1 and Y5 mediate neuropeptide Y induced feeding in the guinea-pig.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Apr;135(8):2029-37. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704667. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11959807 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of neuropeptide Y-induced feeding in mice: do Y1-Y6 receptor subtypes mediate feeding?J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 May;289(2):1031-40. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999. PMID: 10215684
-
Role of the Y1 receptor in the regulation of neuropeptide Y-mediated feeding: comparison of wild-type, Y1 receptor-deficient, and Y5 receptor-deficient mice.Endocrinology. 2000 Mar;141(3):1011-6. doi: 10.1210/endo.141.3.7387. Endocrinology. 2000. PMID: 10698177
-
Molecular characterization of the ligand-receptor interaction of the neuropeptide Y family.J Pept Sci. 2000 Mar;6(3):97-122. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1387(200003)6:3<97::AID-PSC236>3.0.CO;2-E. J Pept Sci. 2000. PMID: 10759209 Review.
-
Central functions of neuropeptide Y in mood and anxiety disorders.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011 Nov;15(11):1317-31. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2011.628314. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011. PMID: 21995655 Review.
Cited by
-
The identification of neuropeptide Y receptor subtype involved in phenylpropanolamine-induced increase in oxidative stress and appetite suppression.Neuromolecular Med. 2013 Mar;15(1):159-68. doi: 10.1007/s12017-012-8206-x. Epub 2012 Nov 20. Neuromolecular Med. 2013. PMID: 23179670
-
Neuropeptide Y in normal eating and in genetic and dietary-induced obesity.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2006 Jul 29;361(1471):1159-85. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2006.1855. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16874931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rational Development of Stable PYY3-36 Peptide Y2 Receptor Agonists.Pharm Res. 2021 Aug;38(8):1369-1385. doi: 10.1007/s11095-021-03077-x. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 34272643
-
Homeostasis in anorexia nervosa.Front Neurosci. 2014 Aug 6;8:234. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00234. eCollection 2014. Front Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25147496 Free PMC article.
-
Receptors for NPY and PACAP differ in expression and activity during adipogenesis in the murine 3T3-L1 fibroblast cell line.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Jun;157(4):620-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00164.x. Epub 2009 Apr 27. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19422400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AMMAR A.A., SEDERHOLM F., SAITO T.R., SCHEURINK A.J., JOHNSON A.E., SÖDERSTEN P. NPY-leptin: opposing effects on appetitive and consummatory ingestive behavior and sexual behavior. Am. J. Physiol. 2000;278:R1627–R1633. - PubMed
-
- BALASUBRAMANIAM A., SHERIFF S., ZHAI W., CHANCE W.T. Bis(31/31′){[Cys31,Nva34]NPY(27–36)-NH2}: a. Peptides. 2002;23:1485–1490. - PubMed
-
- BANNON A.W., SEDA J., CARMOUCHE M., FRANCIS J.M., NORMAN M.H., KARBON B., MCCALEB M.L. Behavioral characterization of neuropeptide Y knockout mice. Brain Res. 2000;868:79–87. - PubMed
-
- BATTERHAM R.L., COWLEY M.A., SMALL C.J., HERZOG H., COHEN M.A., DAKIN C.L., WREN A.M., BRYNES A.E., LOW M.J., GHATEL M.A., CONE R.D., BLOOM S.R. Gut hormone PYY3–36 physiologically inhibits food intake. Nature. 2002;418:650–654. - PubMed
-
- BERGLUND M.M., HOLMBERG S.K.S., ERIKSSON H., GEDDA K., MAFFRAND J.P., SERRADEIL-LE GAL C., CHHAJLANI V., GRUNDEMAR L., LARHAMMAR D. The cloned guinea pig neuropeptide Y receptor Y1 conforms to other mammalian Y1 receptors. Peptides. 1999;20:043–1053. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

