Involvement of Rho-kinase in contraction of guinea-pig aorta induced by prostanoid EP3 receptor agonists
- PMID: 12922932
- PMCID: PMC1573987
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705393
Involvement of Rho-kinase in contraction of guinea-pig aorta induced by prostanoid EP3 receptor agonists
Abstract
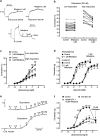
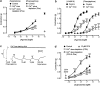
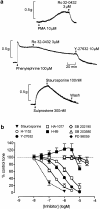
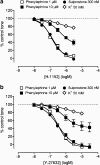
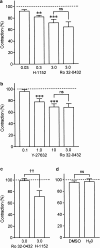
1. The mechanism of contraction of guinea-pig isolated aorta induced by the prostanoid EP(3) receptor agonist sulprostone (0.1-300 nM) has been investigated. In 60% of the experiments, the sulprostone log concentration-response curve (maximum=15-40% of 100 nM U-46619 response; low-responders) was unaffected by the removal of extracellular Ca(2+), blockade of L-type Ca(2+) channels with nifedipine and depletion of internal Ca(2+) stores. In the remaining preparations (35-65% of 100 nM U-46619 response; high-responders), contractions to higher sulprostone concentrations showed a nifedipine-sensitive component, which was enhanced by charybdotoxin. 2. In Ca(2+)-free Krebs solution, established contractions to 300 nM sulprostone were abolished by the Rho-kinase inhibitors H-1152, Y-27632 and HA-1077 (IC(50) values=190, 770 and 2030 nM). The PKA/Rho-kinase inhibitor H-89 (10 nM-10 micro M) caused enhancement progressing to inhibition. The selective PKC inhibitor Ro 32-0432 (3 micro M) had no effect, while staurosporine, recently shown to be a potent Rho-kinase inhibitor, abolished sulprostone responses (IC(50) approximately 47 nM), but its action was slow. The MAP kinase inhibitors SB 202190, SB 203580 and PD 80958 produced little inhibition. 3. In normal Krebs solution, H-1152 and Y-27632 abolished established contractions to 300 nM sulprostone and 1 micro M phenylephrine, and partially inhibited 10 micro M phenylephrine and 50 mM K(+) responses. 4. The results are discussed in relation to the reported potencies of the protein kinase inhibitors in enzyme assays. Activation of the Rho-kinase pathway appears to be a primary mechanism of contraction induced by EP(3) receptor agonists in guinea-pig aorta.
Figures

References
-
- ABRAMOVITZ M., ADAM M., BOIE Y., CARRIÈRE M.-C., DENIS D., GODBOUT C., LAMONTAGNE S., ROCHETTE C., SAWYER N., TREMBLAY N.M., BELLEY M., GALLANT M., DUFRESNE C., GAREAU Y., RUEL R., JUTEAU H., LABELLE M., OUIMET N., METTERS K.M. The utilization of recombinant prostanoid receptors to determine the affinities and selectivities of prostaglandins and related analogs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2000;1483:285–293. - PubMed
-
- ALESSI D.R., CUENDA A., COHEN P., DUDLEY D.T., SALTIEL A.R. PD 98059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:27489–27494. - PubMed
-
- ARNER A., PFITZER G. Regulation of cross-bridge cycling by Ca2+ in smooth muscle. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999;134:63–146. - PubMed
-
- AUDOLY L.P., TILLEY S.L., GOULET J., KEY M., NGUYEN M., STOCK J.L., MCNEISH J.D., KOLLER B.H., COFFMAN T.M. Identification of specific EP receptors responsible for the hemodynamic effects of PGE2. Am. J. Physiol. 1999;277:H924–H930. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

