Receptor-independent activation of Rho-kinase-mediated calcium sensitisation in smooth muscle
- PMID: 12922941
- PMCID: PMC1573988
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705394
Receptor-independent activation of Rho-kinase-mediated calcium sensitisation in smooth muscle
Abstract
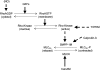
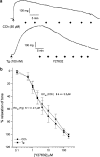
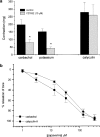
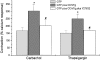
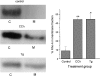
1. The aim of this work was to determine whether Rho-kinase-mediated calcium sensitisation contributes to contractions of the mouse anococcygeus smooth muscle and, if so, whether the process was activated by receptor-dependent or receptor-independent mechanisms. 2. The Rho-kinase inhibitor Y27632 produced concentration-dependent decreases in tone raised by either the muscarinic receptor agonist carbachol (CCh), or the sarco-endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase inhibitor thapsigargin (Tg) (EC(50) values against CCh and Tg of 8.4+/-3.3 (n=6) and 6.1+/-2.1 (n=7) micro M, respectively). Pretreatment of tissues with Y27632 also inhibited contractions produced by 65 mM external potassium (69+/-7% (n=4) inhibition using 10 micro M Y27632). Y27632 had no effect on contractions produced by the inhibitor of smooth muscle myosin light-chain phosphatase, calyculin-A. 3. In beta-escin-permeabilised preparations, both CCh and Tg produced significant increases in tone over-and-above that produced by a combination of calcium (1 micro M) and GTP (100 micro M). These responses to CCh and Tg were inhibited by Y27632 (10 micro M). 4. Western blot analysis of fractionated tissue samples probed for RhoA immunoreactivity, indicated that both CCh and Tg were able to induce translocation of RhoA from the cytosol to the membrane. 5. These findings suggest that Rho-kinase-mediated calcium sensitisation is activated by both receptor-dependent and receptor-independent mechanisms in the mouse anococcygeus.
Figures
References
-
- AYMAN S., WALLACE P., GIBSON A., MCFADZEAN I. The Rho-kinase inhibitor, Y-27632, inhibits contractile responses to carbachol, thapsigargin and potassium in the mouse anococcygeus. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002;137:25P.
-
- CHIBA Y., TAKEYAMA H., SAKAI H., MISAWA M. Effects of Y-27632 on acetylcholine-induced contraction of intact and permeabilised intrapulmonary bronchial smooth muscle in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001;427:77–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

